

Background: Immunoglobulin-A vasculitis (IgAV) is an inflammatory disease characterised by the deposition of immune complexes containing abnormally glycosylated galactose-deficient IgA1 in small blood vessels [1]. Nephritis is the most serious feature of this vasculitis [2], constituting its main cause of long-term morbidity and mortality as well as its main prognostic factor [3]. Unfortunately, renal biopsy is the gold standard for the definitive diagnosis of nephritis, being an invasive and not easily monitored dynamic technique [4]. Accordingly, the identification of sensitive, specific and non-invasive biomarkers of renal damage in IgAV has been of increasing interest over the last decade. In this regard, preliminary data of our group have described the relevance of peripheral B-cells in the renal damage of IgAV, pointing to the methylome profile of these peripheral B-cells as a potential biomarker of this condition.
Objectives: To evaluate whether the transcriptome profile of peripheral B-cells is involved in the development of renal damage in patients with IgAV and, consequently, could be a useful biomarker of this condition, by performing the first exhaustive analysis of the transcriptome.
Methods: 29 Caucasian patients diagnosed with IgAV, who were in the acute phase of the disease, were recruited in this study. Among these patients, 16 (55.2%) developed nephritis. First, peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from all patients by density gradient using Ficol. Subsequently, B-cells were purified using magnetic cell separation by MACS® Technology. Finally, total RNA was extracted from each B-cell and subjected to the TruSeq Stranded mRNA Library Prep Kit (Illumina, CA, USA) and the paired-end sequencing was conducted on a HiSeq sequencer (Illumina, CA, USA).
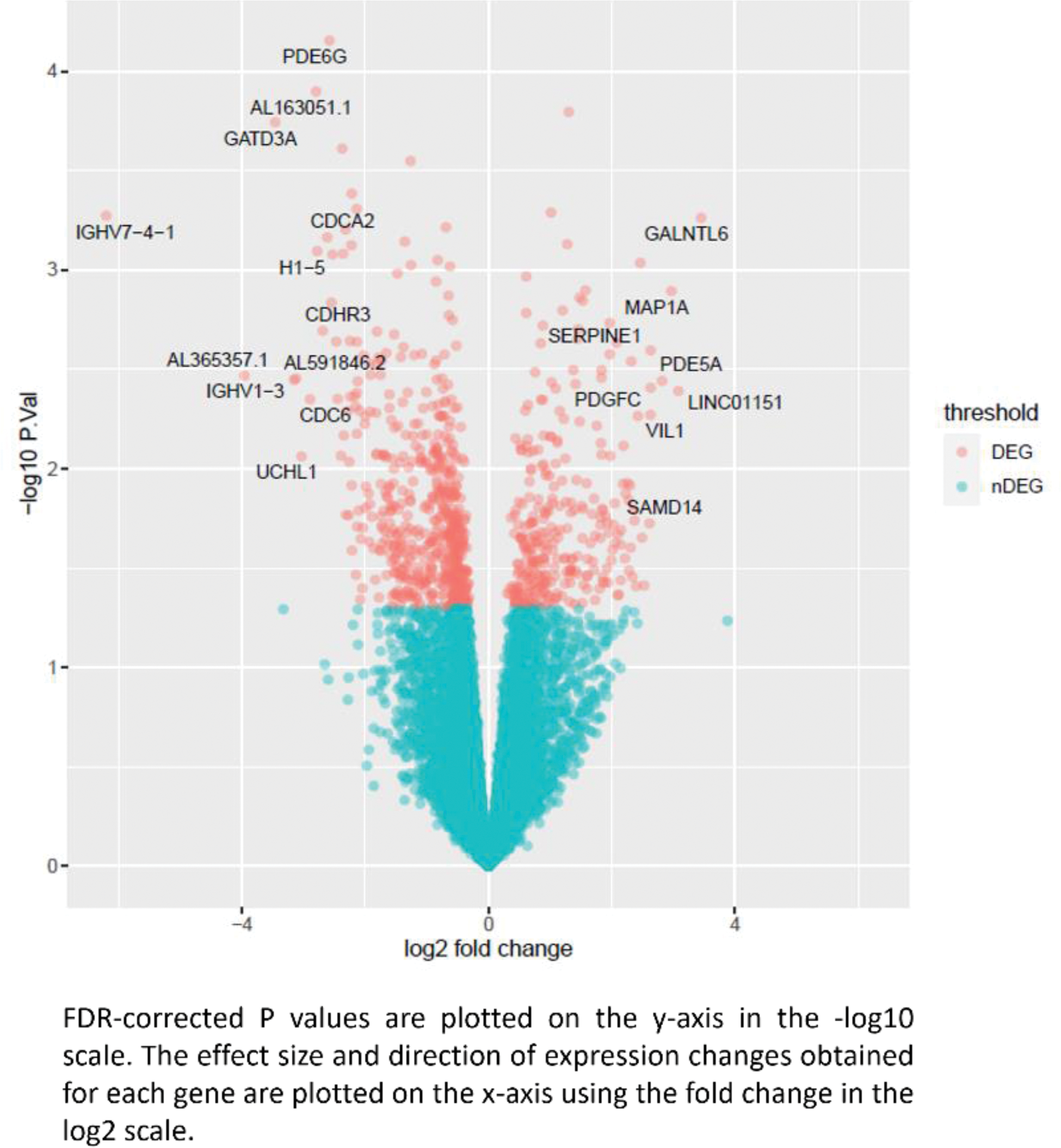
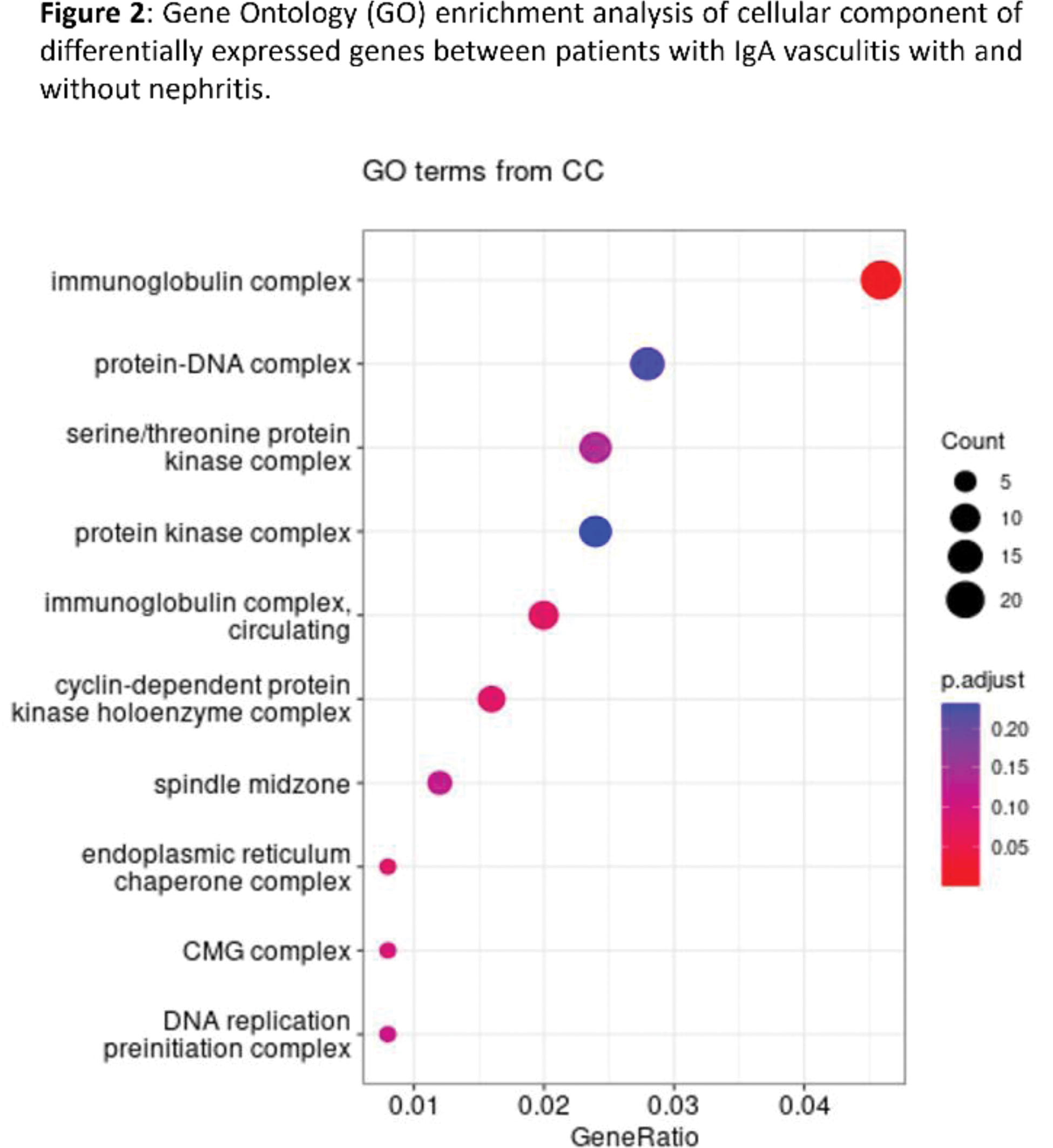
Results: Our preliminary results unveiled profound alterations in the transcriptome profile of peripheral B-cells from patients with IgAV who developed nephritis compared to those IgAV patients without renal damage. In this regard, our results revealed 672 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) across the whole genome between these groups of individuals. Among them, GALNTL6 (gene encodes a molecule involved in protein O-linked glycosylation), as well as MAP1A , SERPINE1 , PDE5A , and PDGFC , were amongst the most significant upregulated DEGs (Figure 1). By contrast, PDE6G, GATD3A, and CDCA2 were amongst the most significant downregulated DEGS (Figure 1). Interestingly, through gene ontology (GO) analysis of these data, we observed an enrichment in several cellular component, highlighting immunoglobulin complex (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Our results point to the transcriptome profile of peripheral B-cells as a biomarker of renal damage in patients with IgAV, highlighting its potential usefulness in clinical practice as a non-invasive additional tool for the definitive diagnosis of nephritis in IgAV.
REFERENCES: [1] Arthritis Rheum .2013;65:1-11.
[2] Autoimmun Rev.2018;17:301-15.
[3] J Am Soc Nephrol.2002;13:1271-8 .
[4] Front Immunol.2022:13:921864.
Acknowledgements: This research was funded by European Union FEDER funds and “Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias” from “Instituto de Salud Carlos III” (ISCIII, Health Ministry, Spain), grant number PI18/00042, PI21/00042 and PI24/00382. JCBL is a recipient of a PFIS program fellowship from the ISCIII, co-funded by the European Social Fund (`Investing in your future´), grant number FI22/00020. RL-M is a recipient of a Miguel Servet type II program fellowship from the ISCIII, co-funded by ESF (“Investing in your future”, grant number CPII21/00004.
Disclosure of Interests: Joao Carlos Batista-Liz: None declared, LAURA CARMEN TERRON CAMERO: None declared, Iván Fernández Rengel: None declared, María Teresa Leonardo Cabello: None declared, Ana Cristina Peñalba Citores: None declared, Luis Martín-Penagos: None declared, Lara Belmar-Vega: None declared, Cristina Gomez-Fernandez: None declared, Ligia Gabrie: None declared, Rafael Gálvez-Sánchez: None declared, Luis Caminal-Montero: None declared, Ana Isabel Turrión: None declared, Diego de Argila: None declared, Esther Vicente-Rabaneda: None declared, Belén Sevilla-Pérez: None declared, José Luis Callejas: None declared, Ana Márquez: None declared, Javier Martin: None declared, Eduardo Andrés-León: None declared, Santos Castañeda: None declared, Ricardo Blanco had consultation fees/participation in company-sponsored speaker´s bureau from Abbvie, Pfizer, Roche, Bristol-Myers, Lilly, Janssen, and MSD, has received grants/research supports from Abbvie, MSD, and Roche, Verónica Pulito-Cueto: None declared, Raquel López-Mejías: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (