

Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease that not only has a high incidence rate but also imposes a heavy burden on society. Over the past few decades, significant progress has been made in the treatment of RA with the advent of various targeted therapeutic agents. Despite the ever-evolving treatment options for RA, many patients still fail to achieve sustained remission, posing a severe challenge for precision therapy in RA.
Objectives: To identify novel biomarkers and latent mechanisms for RA through a comprehensive analysis combining Genome-wide Association Studies (GWAS), Mendelian randomization, and single-cell transcriptomic (scRNA-seq).
Methods: In our study, we first conducted a comprehensive analysis of RA genome-wide association study data (Finngen_R10_M13_RHEUMA, GCST90013534, Ukb-b-11874) and annotated the biological functions and KEGG signaling pathways of genes located around novel loci. Subsequently, we utilized protein quantitative trait loci (pQTL) data from seven cohorts and employed two-sample Mendelian randomization to uncover causal relationships between proteins and RA. Furthermore, we validated the identified genes at the scRNA-seq level in RA, thereby further elucidating the mechanisms underlying the involvement of candidate genes in the pathogenesis of RA.
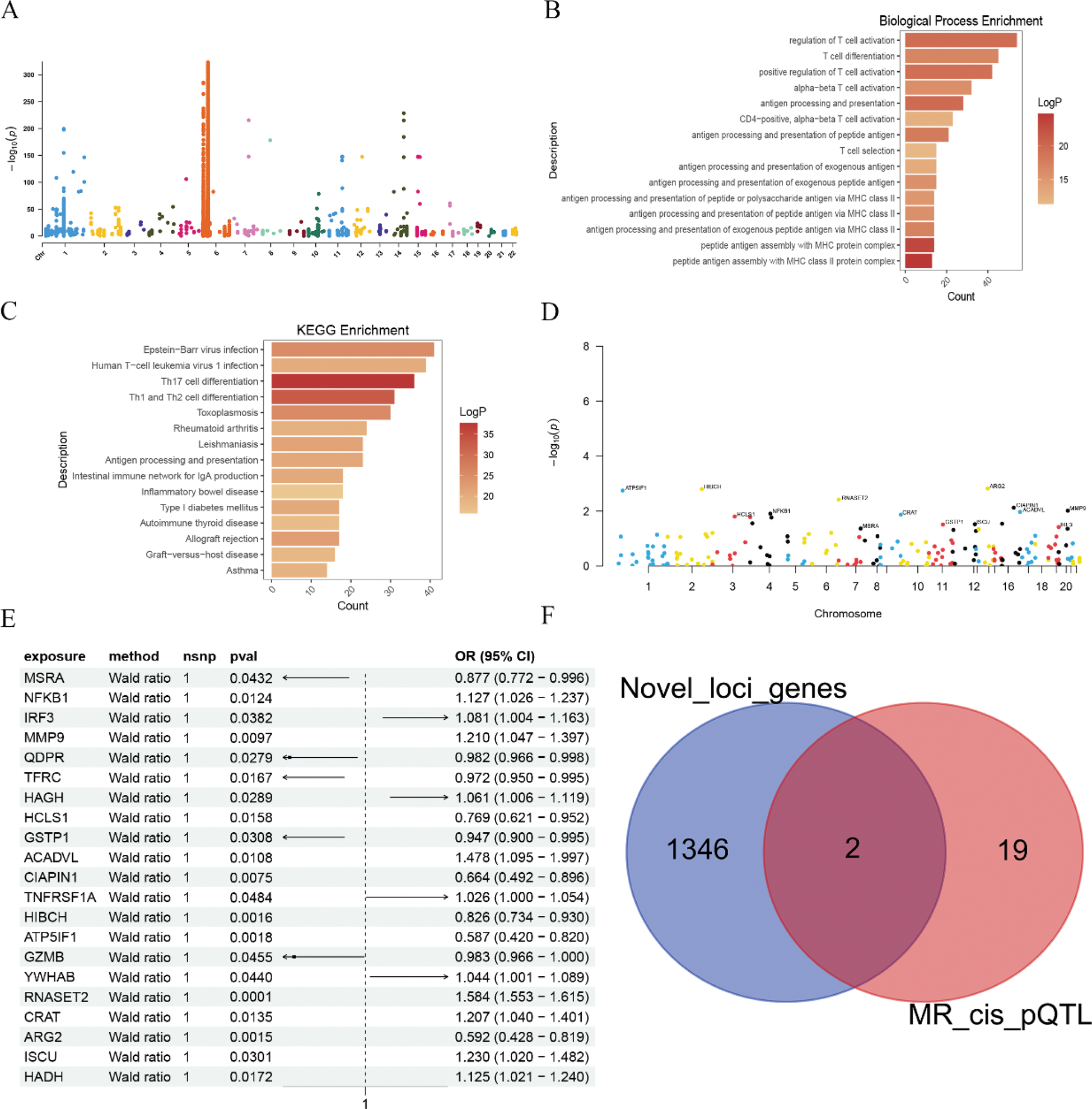
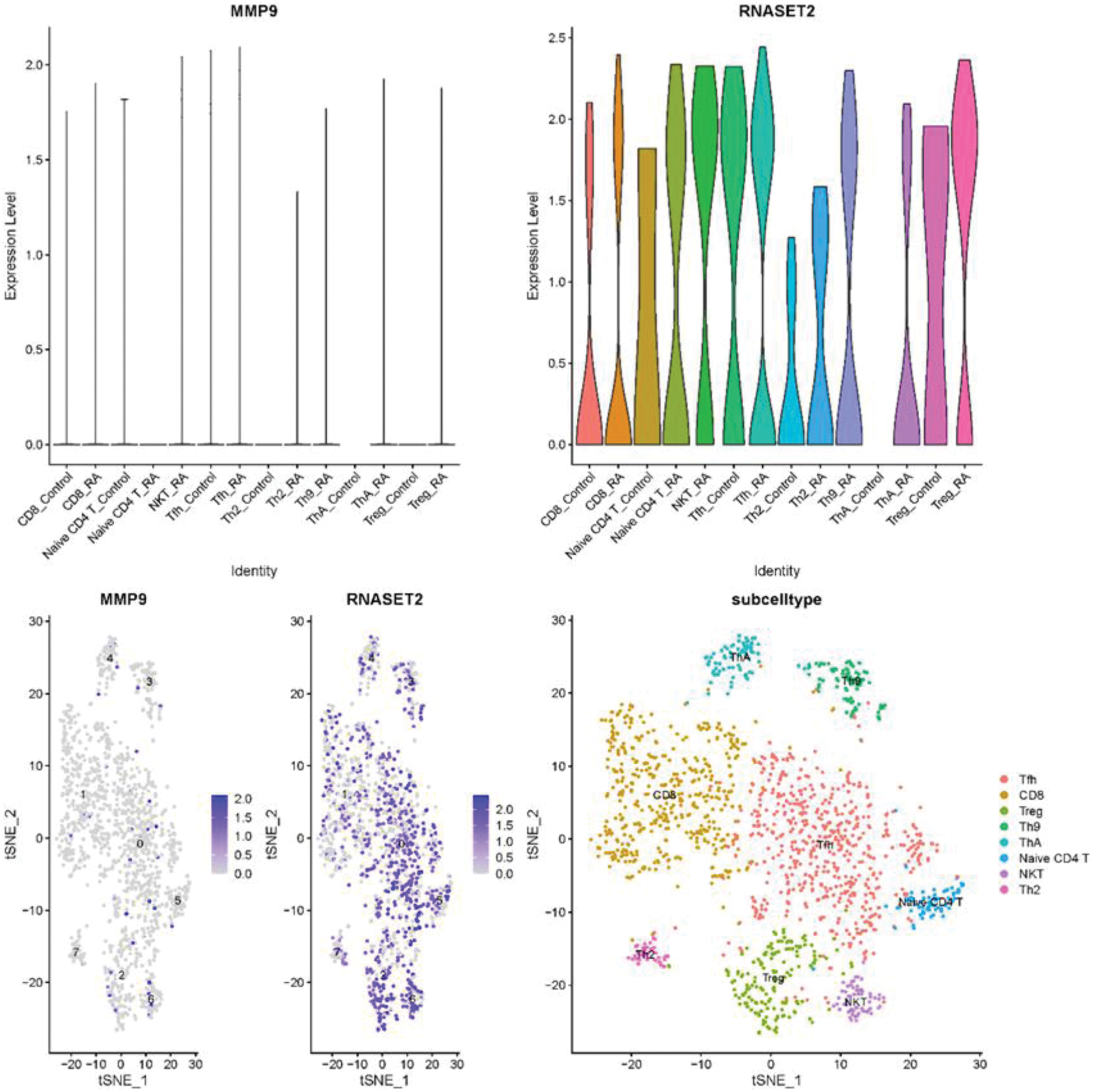
Results: Based on a comprehensive analysis of three RA GWAS datasets, we identified 88 significant loci (P < 5e-08). Subsequent comparison with previously reported loci further revealed 26 novel loci, namely rs76824778, rs1984001, rs56203718, rs11757201, rs72836346, rs7546838, rs66654254, rs7746977, rs11102660, rs77899560, rs10261758, rs9469527, rs175714, rs3108155, rs11066283, rs1569558, rs62242118, rs55842014, rs147684209, rs9976075, rs6565175, rs41264261, rs562854285, rs13180950, rs2045793, and rs74611185. The genes associated with these novel loci were found to be potentially involved in biological functions or signaling pathways such as regulation of T cell activation, T cell differentiation, positive regulation of T cell activation, Th17 cell differentiation, Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation, and rheumatoid arthritis. Subsequently, causal relationships between pQTLs and RA indicated that 21 proteins were causally related to RA, including MSRA, NFKB1, IRF3, MMP9, QDPR, TFRC, HAGH, HCLS1, GSTP1, ACADVL, CIAPIN1, TNFRSF1A, HIBCH, ATP5IF1, GZMB, YWHAB, RNASET2, CRAT, ARG2, ISCU, and HADH (P < 0.05). By intersecting the genes related to the novel loci with the genes encoding proteins causally related to RA, we found that MMP9 and RNASET2 may be important candidate genes in the onset of RA. Finally, after rigorous quality control processing of RA-related scRNA-seq data, we found that both MMP9 and RNASET2 were highly expressed in RA, particularly RNASET2, in CD8 T cells, naive CD4 T cells, Tfh cells, Th2 cells, and Treg cells.
Conclusion: Through a comprehensive analysis combining GWAS, Mendelian randomization proteomics, and scRNA-seq in RA, we have identified two disease-related causative genes, providing potential targets for preventive interventions in RA.
Identify novel loci and genes associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) through genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and Mendelian randomization analysis. A. The Manhattan plot displays significant loci from the GWAS related to RA; B-C. Biological function annotations and KEGG signaling pathways of genes surrounding the novel loci associated with RA; D-E. Utilizing protein quantitative trait loci (pQTL) data derived from seven cohorts, two-sample Mendelian randomization was employed to reveal causal relationships between proteins and rheumatoid arthritis; F. The intersection of genes related to novel loci of RA and genes encoding proteins associated with pQTL.
Expression and distribution of MMP9 and RNASET2 genes in single-cell transcriptome (scRNA-seq) data of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). A-B. Expression of MMP9 and RNASET2 genes in T cell subpopulations from the scRNA-seq of RA. C-D. Distribution of MMP9 and RNASET2 genes in T cell subpopulations from the scRNA-seq of RA.
REFERENCES: [1] Zheng J, Haberland V, Baird D, Walker V, Haycock PC, Hurle MR, Gutteridge A, Erola P, Liu Y, Luo S, Robinson J, Richardson TG, Staley JR, Elsworth B, Burgess S, Sun BB, Danesh J, Runz H, Maranville JC, Martin HM, Yarmolinsky J, Laurin C, Holmes MV, Liu JZ, Estrada K, Santos R, McCarthy L, Waterworth D, Nelson MR, Smith GD, Butterworth AS, Hemani G, Scott RA, Gaunt TR. Phenome-wide Mendelian randomization mapping the influence of the plasma proteome on complex diseases. Nat Genet. 2020 Oct;52(10):1122-1131.
[2] Sun X, Chen B, Qi Y, Wei M, Chen W, Wu X, Wang Q, Li J, Lei X, Luo G. Multi-omics Mendelian randomization integrating GWAS, eQTL and pQTL data revealed GSTM4 as a potential drug target for migraine. J Headache Pain. 2024 Jul 22;25(1):117.
[3] Ding Q, Hu W, Wang R, Yang Q, Zhu M, Li M, Cai J, Rose P, Mao J, Zhu YZ. Signaling pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Feb 17;8(1):68.
Acknowledgements: Thanks to my family and my cats.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (