

Background: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) potentially poses significant risk to pregnancy outcomes. Gestation may exacerbate underlying lupus activity leading to life-threatening consequences mainly due to limited therapeutic options.This case report explores the safety and efficacy of a single dose of rituximab (RTX) in a SLE patient who developed significant disease flare and a new onset of proteinuria during pregnancy.
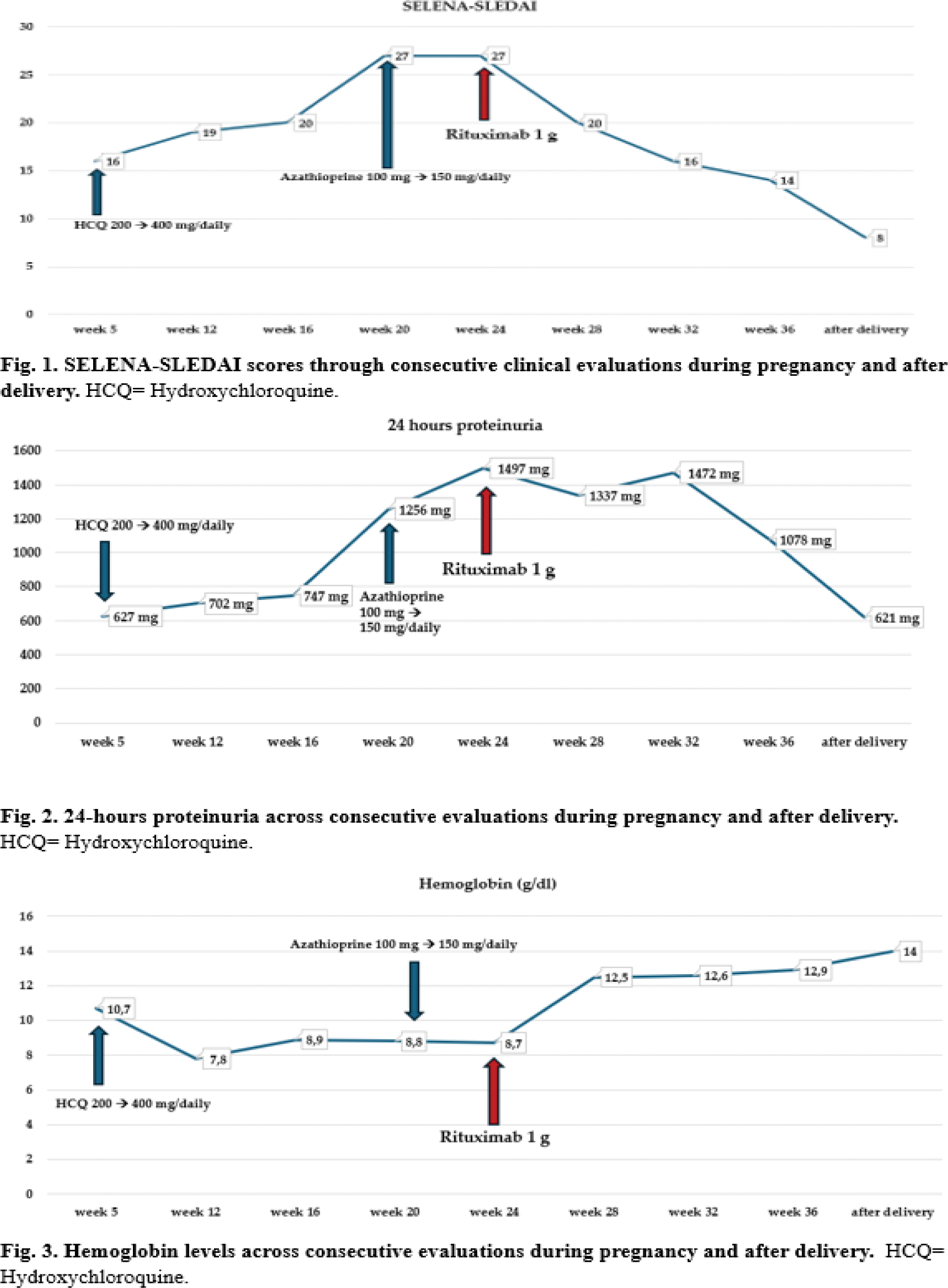
Case presentation: We present the case of a 34-year-old woman diagnosed with SLE and initially treated with hydroxychloroquine (200 mg/daily) and low dose of glucocorticoids. The autoimmune profile revealed positivity for dsDNA, anti-Ro/SSA, anti-La/SSB and antiphospholipid antibodies. The patient had no prior history of pregnancy loss or thrombotic events. In July ‘23, she presented with acute hemolytic anemia necessitating add on therapy with Azathioprine (100 mg/daily). In May ‘24 the patient underwent to an unplanned pregnancy. During a clinical referral at 5 weeks of gestation, elevated disease activity was observed (SLEDAI=16), accompanied by general malaise, fatigue, arthritis, mild anemia and lymphopenia. There were increased inflammatory markers and complement consumption, and a new onset of proteinuria measured at 627 mg/24 hours. At week 12, the patient experienced further clinical worsening, marked by a significant decrease in hemoglobin (Hb) levels (7.8 mg/dL), a notable increase in 24-hours proteinuria (1256 mg) and a rise in the SLEDAI score to 20. This necessitated a rapid escalation of treatment, including full doses of glucocorticoids, azathioprine, hydroxychloroquine and iron supplementation. However, only Hb levels slightly improved to 8.9 mg/dL, while disease activity, inflammatory markers and proteinuria continued to rise until week 24. This prompted the decision to initiate RTX treatment, in a single dose of 1g. The infusion was performed at week 23 and was well-tolerated, without significant complications. Following RTX infusion, at week 28, Hb, complement and inflammatory markers levels showed rapid improvement, while proteinuria remained stable. The delivery occurred preterm at week 36 due to premature rupture of membranes. A healthy male newborn weighed 3010 g with an APGAR of 9. Throughout the pregnancy, the newborn was monitored with fetal echocardiography for potential atrioventricular block and no pathological congenital alterations were detected. 4 weeks postpartum, maternal proteinuria decreased up to 627 mg/24h, Hb increased to 14 mg/dL, while SLEDAI scored 8.
Learning points for clinical practice: To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of a patient receiving RTX for active lupus with new-onset renal involvement during pregnancy. Rituximab may represent a safe and effective therapeutic approach for managing SLE-related manifestations in this complex clinical scenario.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (