

Background: Adult Still’s disease (ASD) is a systemic inflammatory disorder that involves many inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6. Whereas tocilizumab (TCZ), an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, has been shown to be effective for ASD, it suppresses serum CRP levels despite residual disease activity, necessitating alternative methods for assessing ASD disease activity independent of IL-6 pathways.
Objectives: To develop a novel index consisting of proteins that are selected through machine learning, to assess disease activity in patients with ASD under IL-6 inhibition.
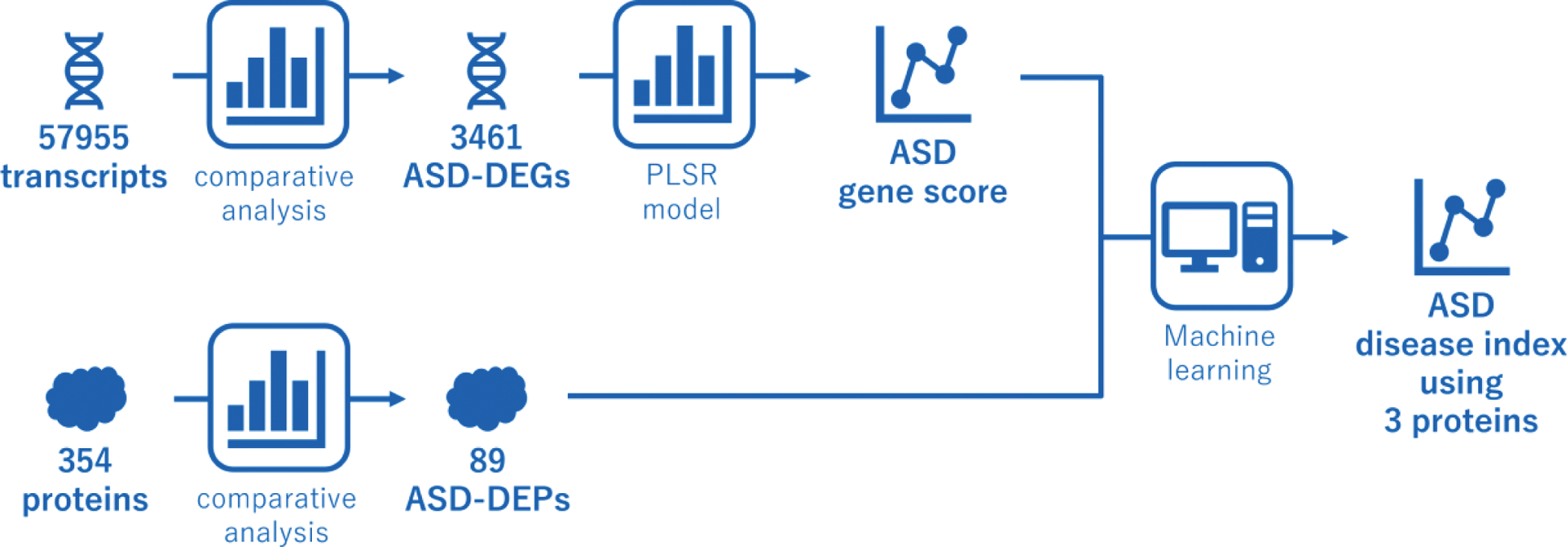
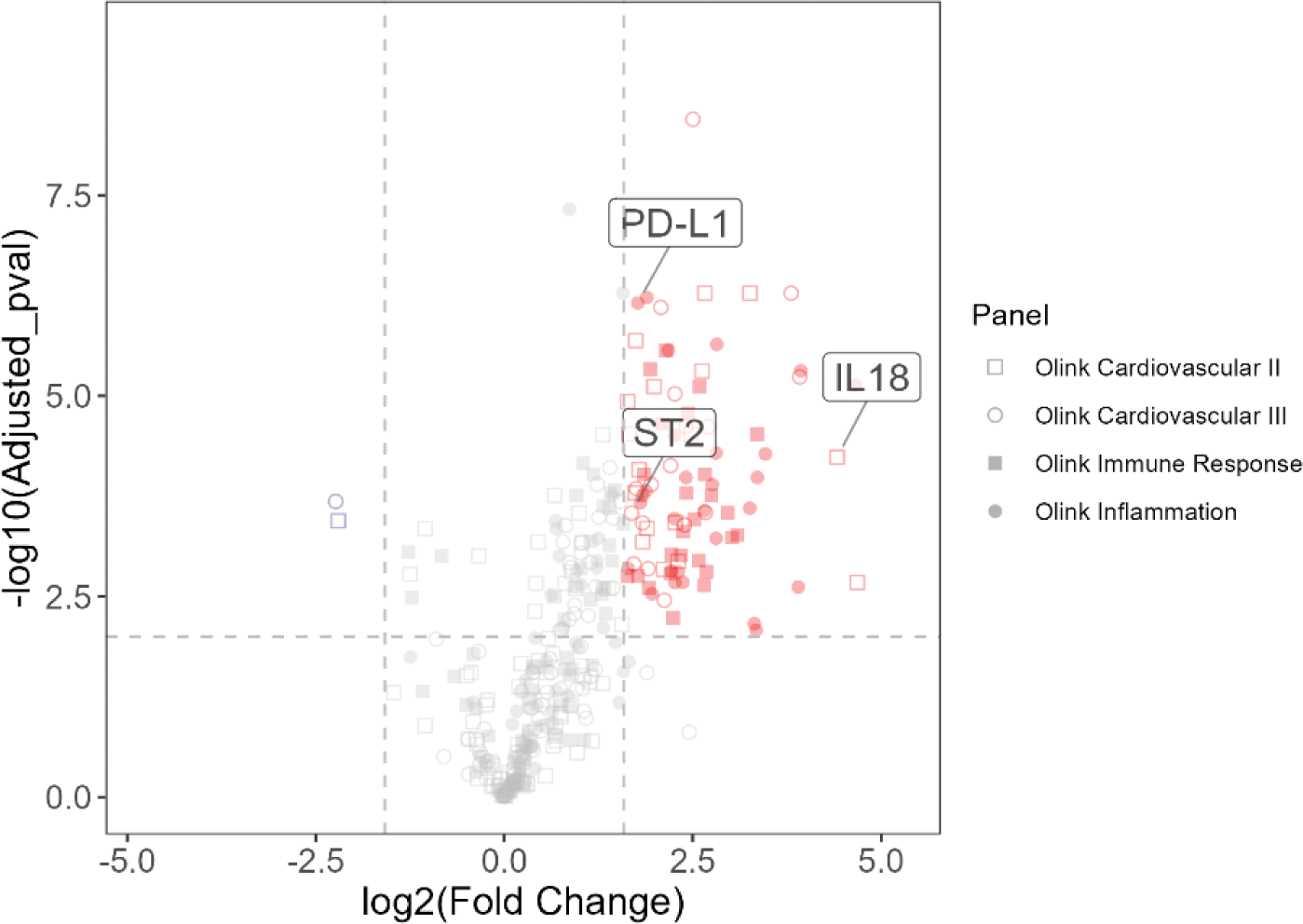
Methods: We conducted a two-step approach with transcriptome and proteomics analyses. First, we performed RNA-seq in the peripheral blood of 53 patients with ASD and 16 healthy controls (HCs) and identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs) for ASD. A partial least squares regression model was constructed using the ASD-DEG expression levels as explanatory variables and disease status (ASD with high activity or HC) as the objective variable. The model output was nominated as the ASD gene score. In the second step, we measured serum concentrations of 354 proteins in 59 patients with ASD and 30 HCs by proteome analysis. To predict the ASD gene score, we developed a random forest model using the ASD gene score as an objective variable and serum protein expression levels as an explanatory variable. Feature selection involved: (1) identifying ASD-differentially expressed proteins (ASD-DEPs) by comparing ASD patients with high disease activity with HCs (Figure 2), (2) calculating correlation coefficients between ASD-DEPs, (3) conducting an exhaustive feature selection for optimal combinations of ≤5 proteins based on Random Forest Regressor, and (4) creating partial dependence plots to exclude low-contribution proteins.
Results: We constructed the ASD gene score using 3461 gene expression, which demonstrated a satisfactory ability to discriminate the disease state in ASD patients, regardless of tocilizumab use, both in the training and validation cohorts. Longitudinal sample analysis revealed that patients showing stable and low ASD gene scores were in sustained remission. Furthermore, the ASD gene score was elevated in clinically active patients who were treated with TCZ and showed normal CRP levels, suggesting the ASD gene score can detect disease activity of ASD irrelevant to IL-6 pathways. A random forest model with proteome analyses revealed that the ASD gene score was represented by three proteins, IL-18, IL-33R (ST2), and PD-L1. The algorithm with those proteins computed an index that reflected the disease activity of ASD. Time-series analysis showed that a stable decrease in the index suggested complete remission, while its insufficient reduction predicted relapse, regardless of TCZ administration. The output of this model was termed the ASD disease index.
Conclusion: We developed a random forest model using three proteins and computed a novel index, the ASD disease index, that is useful to assess ASD disease activity independently of IL-6 inhibition. The ASD disease index is also promising in evaluating complete inactive disease and predicting relapse risk in ASD.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Schematic Overview of the Machine Learning Pipeline
Volcano Plot of DEPs in the Active AOSD Compared to the HCs.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Mayu Magi Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Hiroto Yoshida Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Hiroya Tamai: None declared, Kotaro Matsumoto: None declared, Keiko Yoshimoto: None declared, Mitsuhiro Akiyama: None declared, Yasushi Kondo: None declared, Jun Kikuchi: None declared, Yoshihiro Matsumoto Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Tetsuhiro Soeda Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Yuko Kaneko Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (