

Background: Women with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) likely to present decreased functional status and quality of life compared to men [1]. Pilates exercises were shown to be a safe and effective therapeutic approach for managing various rheumatic diseases, yielding significant improvements in clinical outcomes such as functional status, spinal mobility, fatigue, disease activity, pain, and quality of life [2]. However, the effects of Pilates, a broadly preferred exercise approach by women, on PsA remain unexplored.
Objectives: The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of a 12-week mat Pilates exercise program on physical performance and related parameters in women with PsA.
Methods: Forty-eight women with PsA were randomly divided into two groups as Pilates (n=24) and control (n=24) following the baseline measurements. Participants in both groups continued their routine pharmacological treatment. Participants in the Pilates group additionally participated in a progressive mat Pilates exercise program, conducted in groups of eight, twice weekly for 12 weeks under the supervision of a physiotherapist. No additional intervention was provided to the control group. All participants were assessed for physical performance and related parameters as functional status, trunk muscle endurance, disease activity, spinal mobility, fatigue, emotional status, and disease-related quality of life at baseline and after 12 weeks by an evaluator blinded to group allocation.
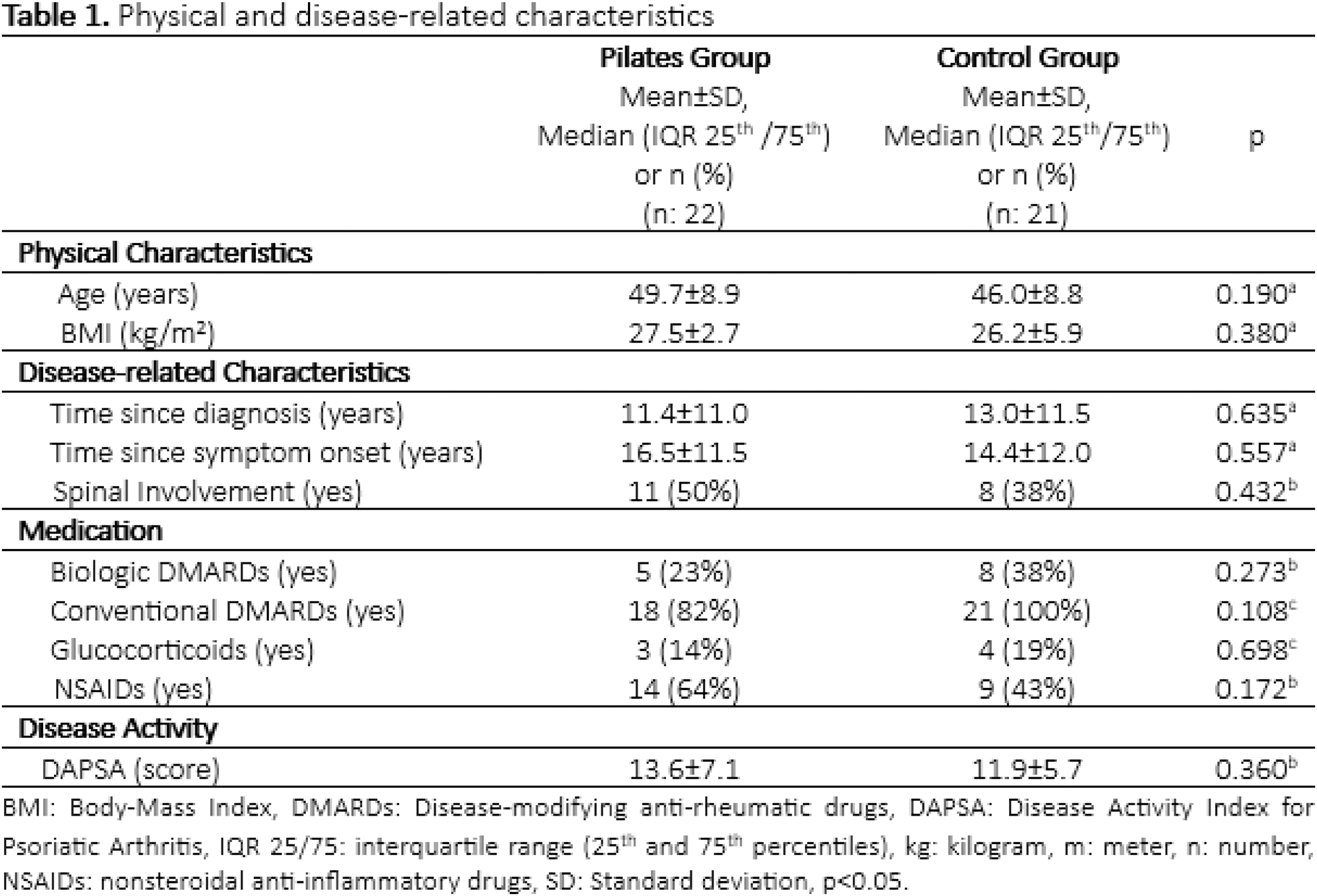
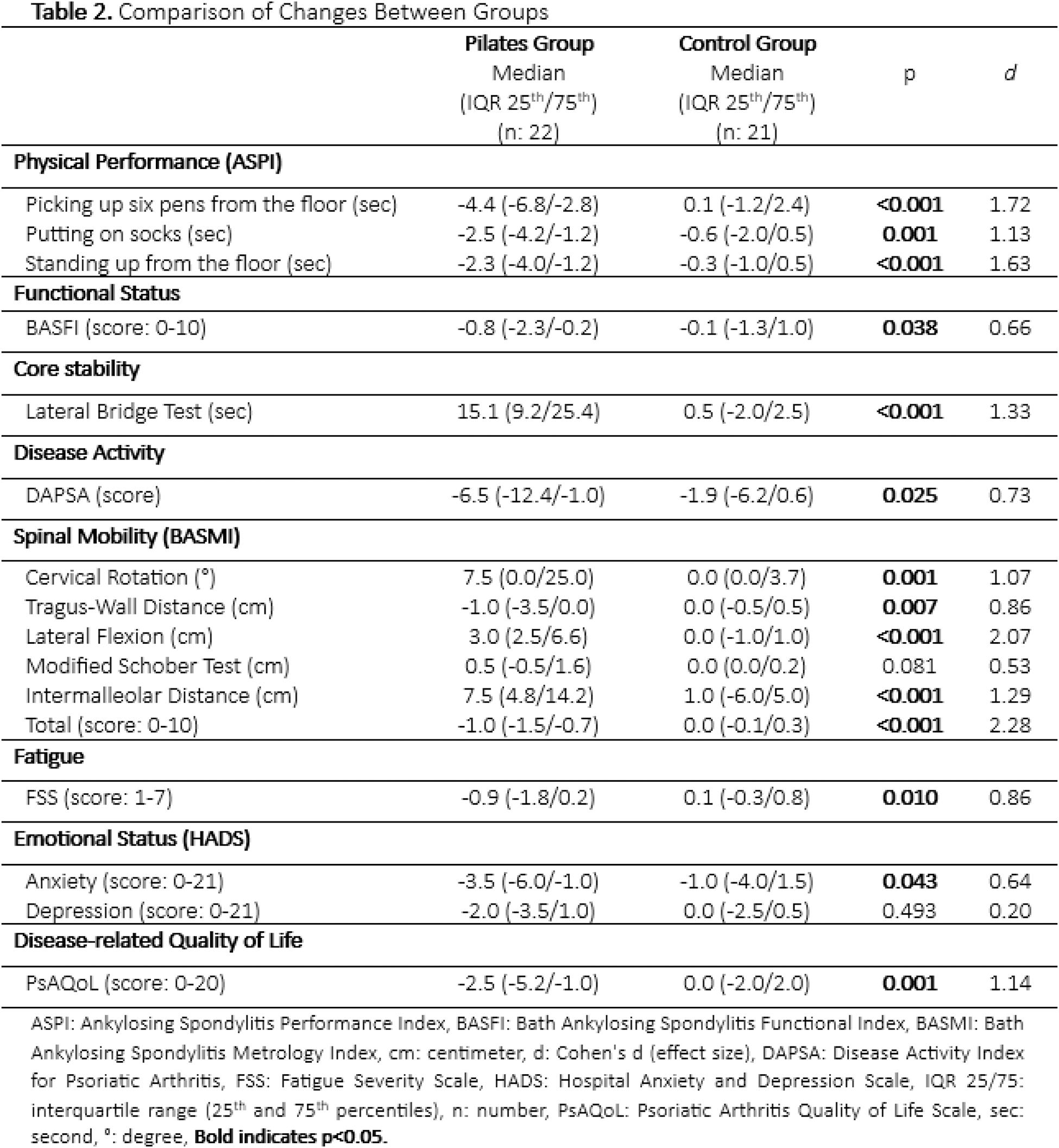
Results: The study was completed with a total of 43 women with PsA (Pilates group=22, control group=21). Groups were similar at the baseline regarding physical and disease-related characteristics (p>0.05, Table 1). Comparison of changes observed during the study revealed that the Pilates group demonstrated significantly greater improvements (p<0.05, Table 2) than the control group across all evaluated parameters, except for spinal mobility in the flexion direction and depression scores (p<0.05, Table 2).
Conclusion: According to our results, a 12-week Pilates exercise program performed twice a week as a group exercise in addition to routine pharmacological treatment may help women to achieve additional benefits for improving physical performance and related parameters.
REFERENCES: [1] Eder L, Thavaneswaran A, Chandran V, Gladman DD. Gender difference in disease expression, radiographic damage and disability among patients with psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis . 2013;72(4):578-582.
[2] Altan L, Korkmaz N, Dizdar M, Yurtkuran M. Effect of Pilates training on people with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(7):2093-2099.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (