

Background: Soluble (s) and membrane-bound (m) tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signal through TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1) and receptor 2 (TNFR2), respectively. At physiological concentrations, sTNF activates the pro-inflammatory TNFR1 pathway but not the TNFR2 pathway, which plays a key role in immune homeostasis, tissue regeneration, and host defense against pathogens and is essential for T reg cell survival, proliferation, and function. Marketed TNF inhibitors, such as adalimumab, inhibit both TNFR1 and TNFR2 signal and block mTNF-dependent T reg expansion. Balinatunfib (SAR441566) is a next generation, small molecule, oral TNFR1 signal inhibitor that selectively binds to sTNF trimer and inhibits signaling via TNFR1, but not via TNFR2. In a Phase I, proof-of-mechanism study, balinatunfib demonstrated clinical efficacy in mild-to-moderate psoriasis over a 4-week treatment period [1].
Objectives: This in vitro study evaluated the effect of balinatunfib on mTNF and IL-2-induced T reg expansion versus other anti-TNF biologics.
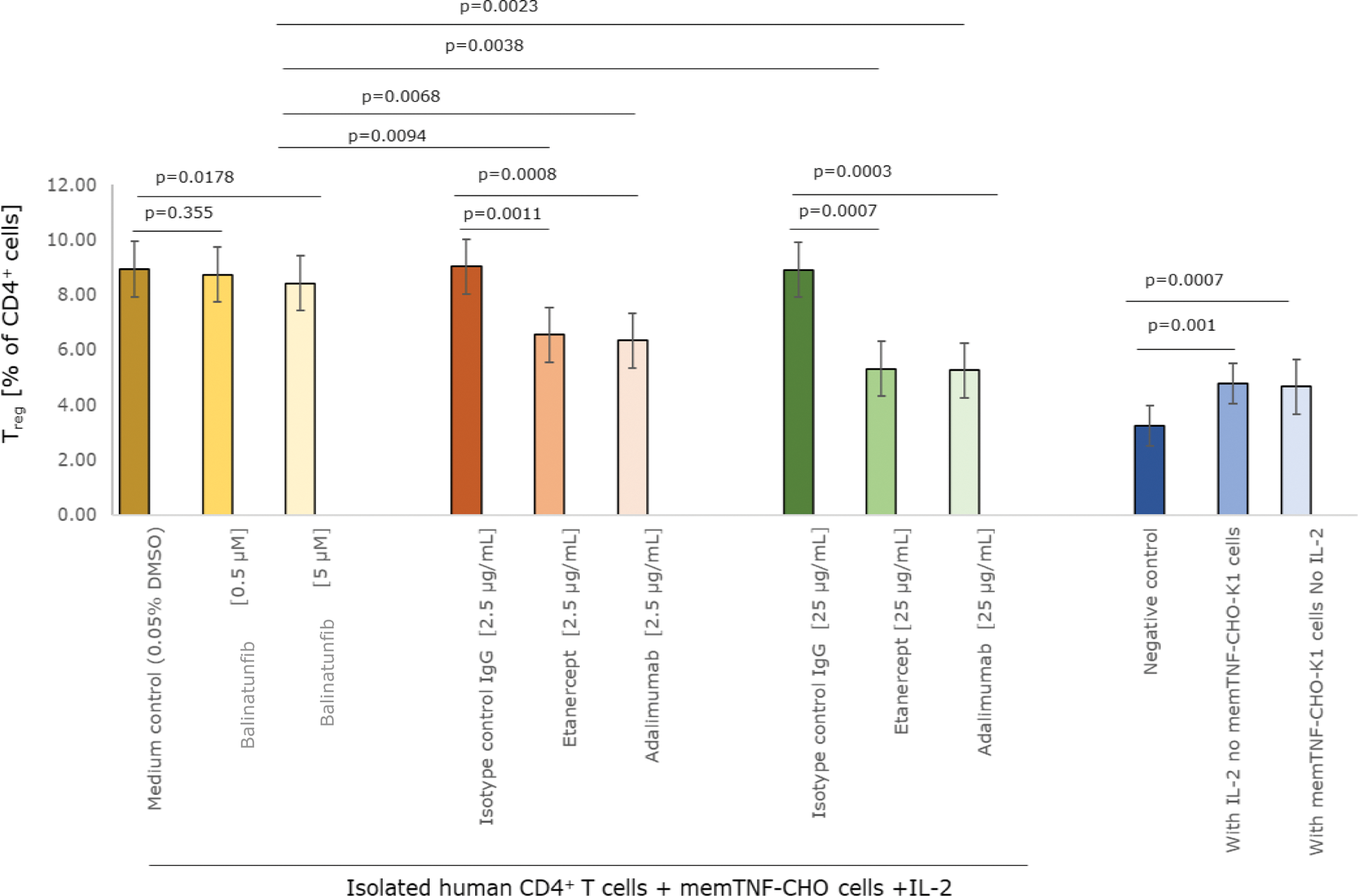
Methods: Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from whole blood samples obtained from healthy volunteers via gradient centrifugation. CD4 + T cells were isolated from PBMCs using a CD4 + T cell isolation kit. memTNF-CHO-K1 cells expressing a mutant variant of mTNF (memTNF), which is resistant to cleavage by the metalloprotease ADAM17, were co-cultured with CD4 + T cells in X-VIVO-15 medium for 48h with/without recombinant IL-2. Induction of CD45 + CD4 + CD25 + FoxP3 + T reg cells was assessed with/without balinatunfib (0.5 μM or 5 μM) or the anti-TNF biologics etanercept or adalimumab (2.5 μg/mL or 25 μg/mL), using flow cytometry. Cells were incubated with fluorescently labeled antibodies for flow cytometry measurements using the LSRFortessa. Mean±SD from triplicate measurements each performed from five donors are presented.
Results: The proportion of T reg cells in unstimulated CD4 + T-cell culture was 3.24±0.74% that increased in the presence of either IL-2 (4.77±1.17%) or when co-cultured with memTNF-CHO-K1 cells (4.65±0.96%) alone. A significant and additive expansion of T reg numbers was observed when co-cultured with memTNF-CHO-K1 cells and in presence of IL-2 (8.99±1.59%, p<0.0001). When co-cultured with IL-2 and balinatunfib (0.5 μM or 5 μM), T reg levels remained high and were largely similar to the corresponding 0.05% DMSO control (Figure 1). However, when co-cultured with IL-2 and etanercept (2.5 μg/mL or 25 μg/mL) or adalimumab (2.5 μg/mL or 25 μg/mL), T reg levels were significantly reduced (by 27.5%-41.06%; p<0.01 for all) versus the respective isotype control (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Treatment with balinatunfib that selectively binds to sTNF and inhibits TNFR1 signal does not inhibit the mTNF–TNFR2 mediated induction of T reg cells, confirming TNFR2 signal sparing by balinatunfib.
Induction of CD45 + CD4 + CD25 + FoxP3 + T reg cells in co-culture with memTNF-CHO cells for 48h in the presence or absence of TNFR1 signalling inhibitor balinatunfib, or the TNF blocking biologics etanercept and adalimumab. Triplicate measurements were performed from five donors. Descriptive statistics were applied and expressed as mean±SD. p-values were based on ANOVA for repeated measures test following the Newman-Keuls and Dunnett’s post-hoc test for respective treatment comparisons.
REFERENCES: [1] Matos T, et al. Efficacy and safety of a small molecule with innovative inhibition of TNFR1 signalling in plaque psoriasis: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. EADV 2023, October 11-14.
Acknowledgements: Balinatunfib was identified in a research collaboration with UCB. This study was funded by Sanofi. Medical writing/editorial assistance was provided by Himanshi Bhatia, PhD, of Sanofi, according to the Good Publication Practice.
Disclosure of Interests: Gertrud Sibenhorn Sanofi, Markus Kohlmann Sanofi, Tiago R. Matos Sanofi, Thomas Leeuw Sanofi.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (