

Background: Takayasu Arteritis (TA) is an autoimmune large-vessel vasculitis with characteristic chronic granulomatous arteritis, with an unclear pathogenesis [1, 2]. Fulminant inflammation of the aortic wall during disease activity has led us to wonder about the mechanism. Pyroptosis is a form of inflammatory cell death, defined as gasdermin-mediated programmed necrosis [3]. It is characterized by the formation of membrane pores, cell swelling, rupture, and the subsequent release of pro-inflammatory cellular contents [4]. To elucidate the mechanism underlying the inflammatory response in the vascular wall of TA, we performed single-cell RNA sequencing of human aortic tissue, revealing the macrophage pyroptosis plays a key role in the progression of TA.
Objectives: The research is to elucidate the role of GSDME-mediated macrophage pyroptosis in the pathogenesis of TA.
Methods: We obtained human aortic tissue samples from patients with atherosclerosis (n=3) or TA (n=3) who underwent aortic replacement surgery in Beijing Anzhen Hospital. Samples suspected of infection were excluded. In vitro experiments involved the isolation of monocytes from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of healthy controls (n=26) and TA patients (n=46). Patients with TA complicated by severe infections, malignancies, neurological disorders, or other autoimmune diseases were excluded. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and immunohistochemistry (IHC) were used to investigate the role of macrophages in the aortic tissues of TA patients and controls. Flow cytometry was employed to evaluate the accompanying inflammatory amplification. The expression and activation of GSDME and Caspase-3 were analyzed through IHC and immunofluorescence. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was performed to assess the expression and role of GSDME in TA.
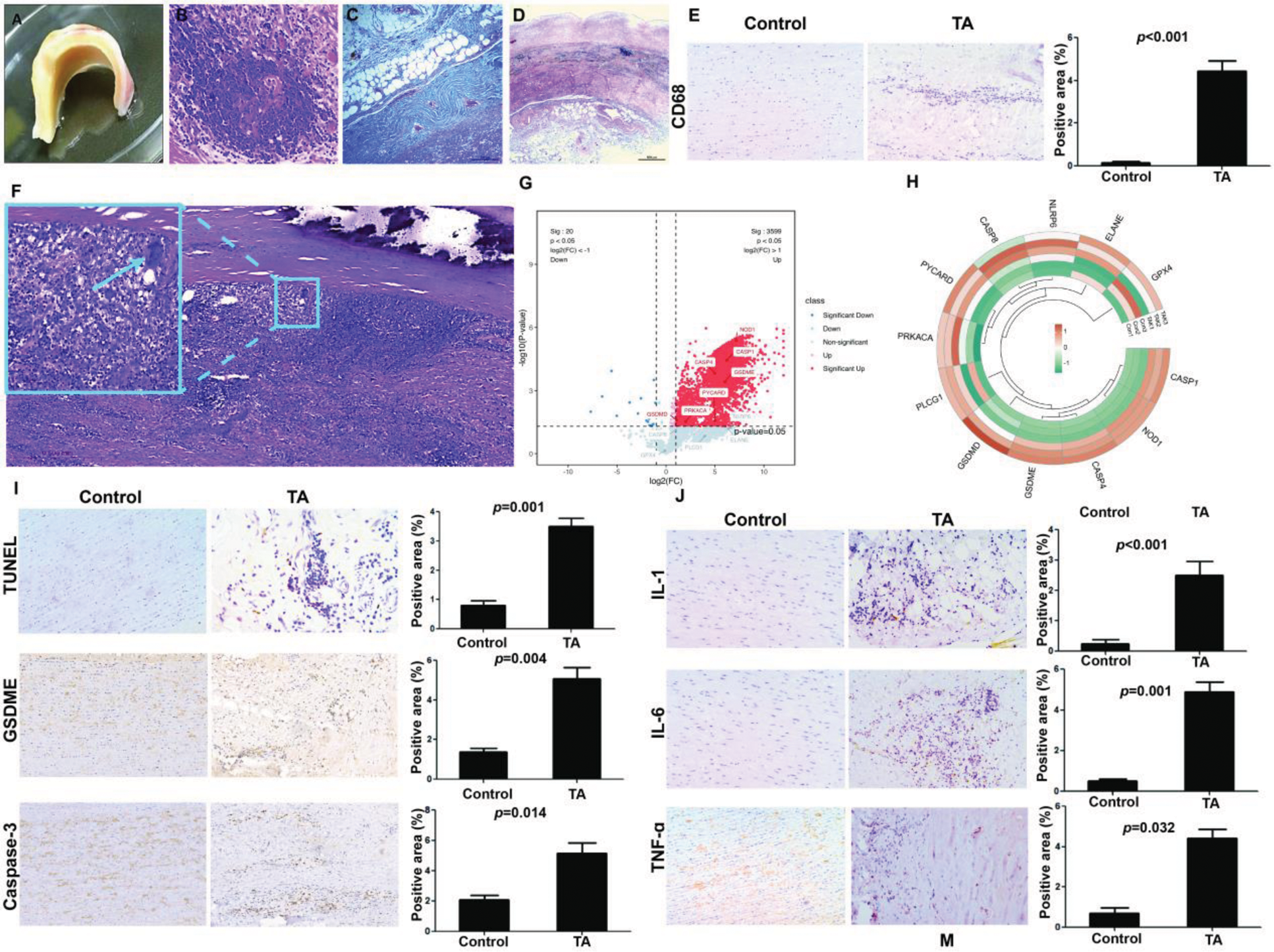
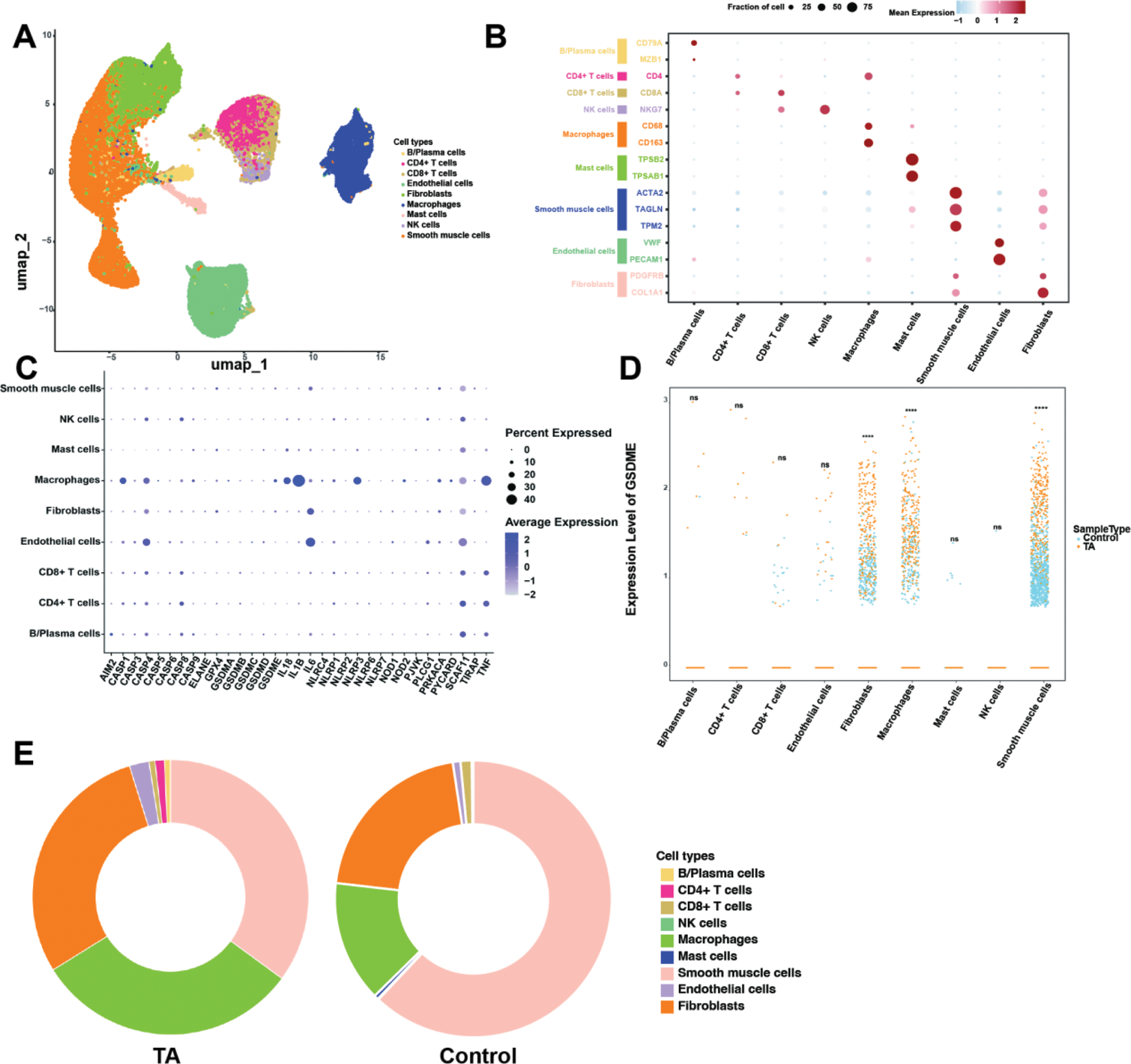
Results: Chronic vascular inflammation is a hallmark of TA. The significant thickening of the aortic wall was observed, and we noted extensive infiltration of inflammatory cells, collagen deposition, and disorganized elastic fibers (Figure 1A-D). Compared to the atherosclerosis control group, macrophages in the aortic tissues of TA patients were significantly increased (Figure 1E-F). To further explore the role of pyroptosis in TA, proteomic sequencing revealed a significant upregulation of pyroptosis-related proteins in TA, especially GSDME (Figure 1G-H). The tunel-positive rate, GSDME and caspase-3 expression in TA patient tissues compared to controls, indicating increased cell death in TA lesions (Figure 1I). Inflammatory factors were shown to be significantly elevated in TA (Figure 1J). Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis was conducted and nine distinct cell clusters with their specific marker genes were shown in Figure 2A-B. We found the expression of classical pyroptosis genes was most prominent in macrophages (Figure 2C). GSDME was significantly increased in macrophages from TA patients, and the expression level of GSDME in TA macrophages was significantly higher than in controls (Figure 2D-E).
Conclusion: These findings provide strong evidence for the pathogenic role of GSDME-mediated macrophage pyroptosis in TA and uncover a novel mechanism involving GSDME in the disease’s pathogenesis. Moreover, targeting GSDME could represent a promising therapeutic approach for TA.
REFERENCES: [1] ARNAUD L, HAROCHE J, MATHIAN A, et al. Pathogenesis of Takayasu’s arteritis: a 2011 update [J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2011, 11(1): 61-7.
[2] KONG X, XU M, CUI X, et al. Potential Role of Macrophage Phenotypes and CCL2 in the Pathogenesis of Takayasu Arteritis [J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 646516.
[3] SHI J, GAO W, SHAO F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death [J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2017, 42(4): 245-54.
[4] WEI Y, LAN B, ZHENG T, et al. GSDME-mediated pyroptosis promotes the progression and associated inflammation of atherosclerosis [J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 929.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82270427); Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7232038); Beijing Anzhen Hospital High Level Research Funding (2024AZC3005). I would like to give my heartfelt thanks to all the people who have ever helped me in this paper. My sincere thanks go firstly to my supervisors, Dr. Lili Pan and Dr. Taotao li for their suggestions and encouragement. I am also grateful to my friend, Mr. Bin Xu for his unwavering support and unfailing love.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (