

Background: Therapy to induce remission as well as subsequent maintenance therapy for AAV is often associated with the long-term use of glucocorticoids. Since the market introduction of avacopan in Germany in March 2022, it has become increasingly possible to discontinue GC during the course of therapy. The necessity of the therapy duration of avacopan, which is generally intended for 12 months, remains critical. The benefit of GC discontinuation under avacopan has been proven with reduced complication rates, especially with regard to infections and osteoporosis, but the risk assessment of AAV recurrence after GC discontinuation following avacopan cessation remains unclear.
Objectives: GC free remission of AAV in maintenance therapy after discontinuation of avacopan.
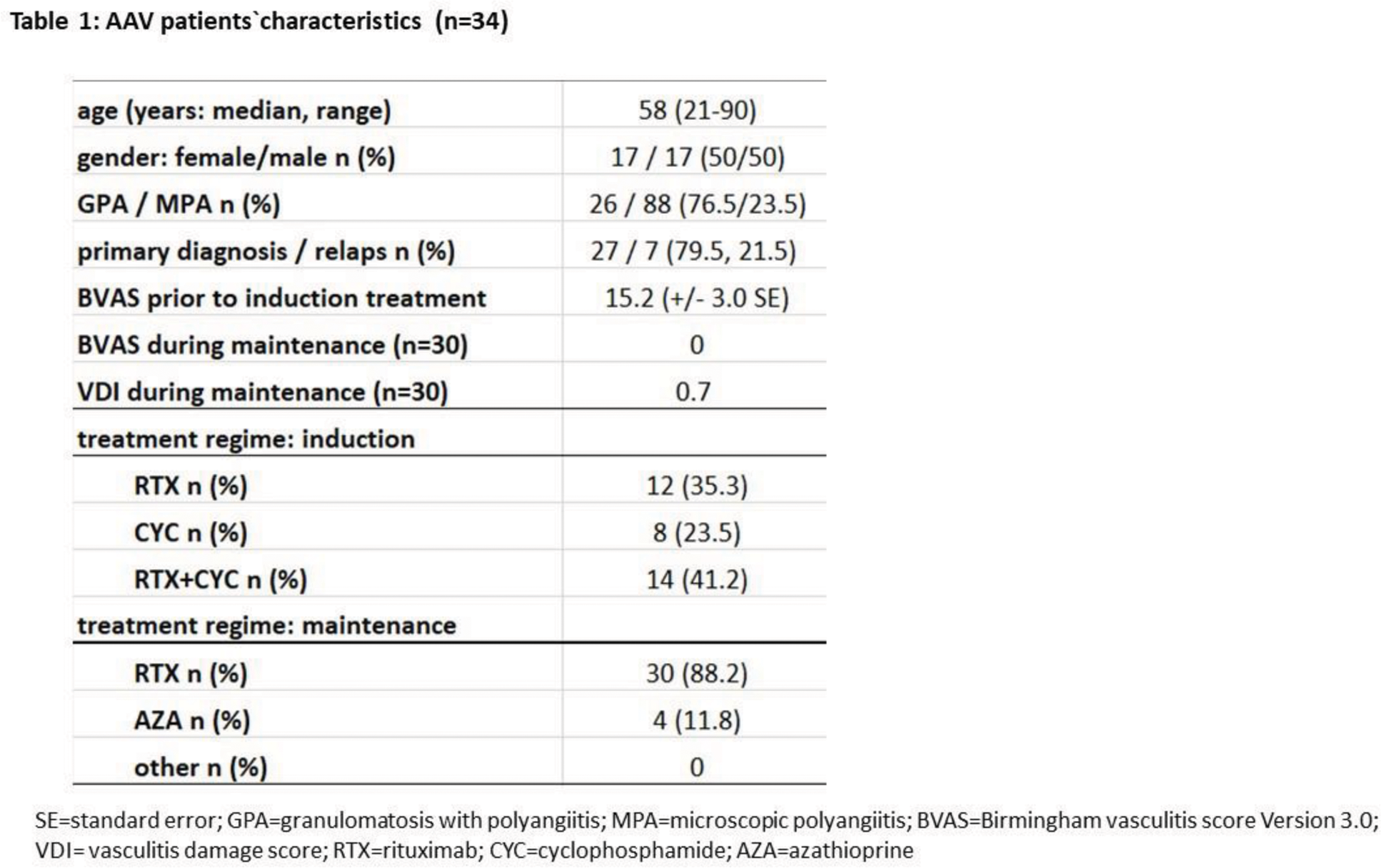
Methods: From March 2022 to January 2024, 86 patients with AAV were treated at Minden University Hospital (in the Department of Rheumatology and the Department of Nephrology), 34 of whom underwent remission induction with cyclophosphamide (CYC), rituximab (RTX) or a combination of CYC/RTX and avacopan. In all patients (n=34) who received avacopan immediately or in the course of therapy, high-dose GC was initially used, which was tapered off within 8-24 weeks under avacopan depending on the clinical course, avacopan itself was stopped between month 11-14. The therapy concept was individually adapted by the physician, the follow-up was carried out prospectively every 3 months with determination of the Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score=BVAS (3.0), VDI (vasculitis damage score) and documentation of the continuation or discontinuation of the medication of avacopan and GC. Table 1 shows the characteristics of the patients (n=34) under therapy in December 2024. All patients were either PR3 or MPO positive and fulfilled the classification criteria of AAV by ACR/EULAR 2022.
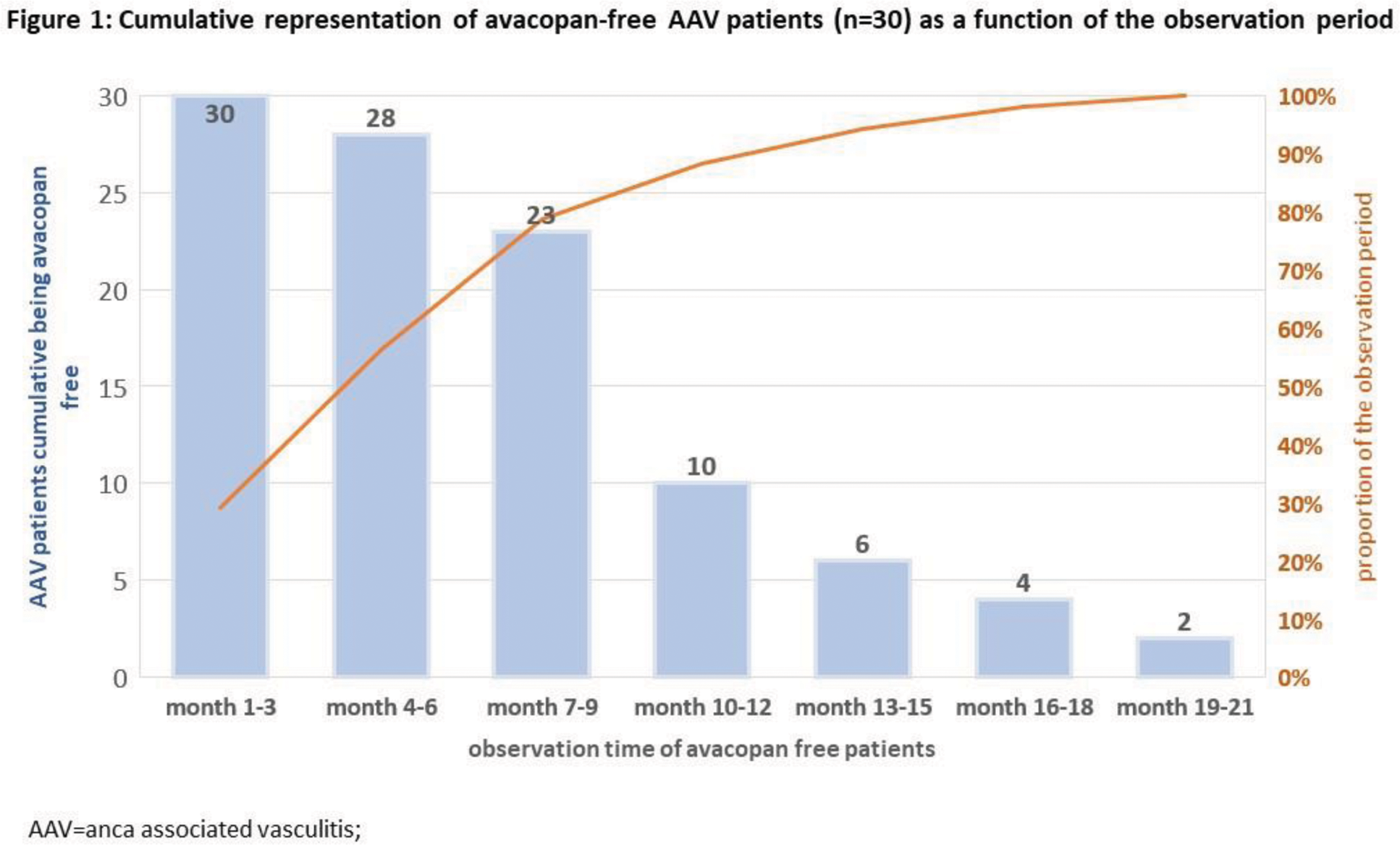
Results: The observation period of the AAV patients (n=34) was 18.9 (± 3.2 standard error, SE) months, of which 15.6 (±2.9 SE) were in maintenance therapy, avacopan was taken for an average of 11.3 (range 1-14) months, whereby avacopan was terminated prematurely in 4 patients (intolerance n=2, relapses and subsequent resumption of GC pulse therapy n=2). At the end of the observation interval, the AAV patients were GC free for a mean of 11.6 (±2.4 SE) months and 6.8 (±2.1 SE) months avacopan free, in each case without evidence of disease activity. Figure 1 shows the cumulative representation depending on the observation period of the GC free and at the same time avacopan free patients (n=30), while the 4 patients with side effect-related discontinuation of avacopan and disease recurrence were not included in the Figure 1.
Conclusion: Following the introduction of avacopan into the AAV treatment regime, a significant number of patients achieved GC free remission within 18 months, even after stopping avacopan. However, a longer observation period and larger cohorts should confirm this observation.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Gunter Assmann Boehringer Ingelheim, CLS Vifor Pharm, Astrazeneca, UCB, AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, CLS Vifor Pharm, Astrazeneca, UCB, AbbVie, UCB, AbbVie, Essert Wiebke: None declared. Turkiewicz Ryszard: None declared. Boll Alina: None declared. Schneider Claus: None declared. Radermacher Joerg: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (