

Background: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease characterized by a strong genetic predisposition, primarily driven by the HLA-B27 allele along with over 100 additional loci identified through genome-wide association studies (GWAS). Since most association signals lie in non-coding regions, identifying causal variants and understanding their functional roles remain key challenges in the post-GWAS era. CARD9 encodes an adaptor protein essential for coordinating innate and adaptive immune responses to pathogens, activating NF-κB and MAP kinase pathways to promote proinflammatory cytokine production and Th17 differentiation which are central to axSpA pathogenesis. Although variants in the CARD9 locus have been associated with axSpA, the specific causal variant(s), their mechanisms of action, and their functional consequences remain unknown.
Objectives: To identify the functional basis for the genetic association of CARD9 variants with axSpA and its consequences on proinflammatory cytokines production.
Methods: Bayesian fine mapping was performed on the CARD9 locus using the British subset of the IGAS Immunochip case-control GWAS [1]. To evaluate the regulatory functions of candidate causal variants, expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) and chromatin accessibility quantitative trait loci (caQTL) mappings were carried out using RNAseq and ATACseq data in three immune cell types dysregulated during SpA (CD14+ monocytes, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells) from 45 individuals (20 axSpA, 35 healthy controls (HC)) [2]. ATAC-seq footprinting was then applied using Tobias [3] to identify transcription factor binding site potentially disrupted by candidate causal variants, leveraging publicly available ATAC-seq data of CD14+ cells from 41 HC [4]. Finally, TNFα, IL-6 and IL-23 production was quantified by flow cytometry in monocytes from 59 axSpA patients before and after 18 hours of stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or Candida albicans (C.alb). The influence of candidate variant genotypes on this secretion was assessed with linear regression including age, sex, cell mortality, stimulation, and biologics use as covariates.
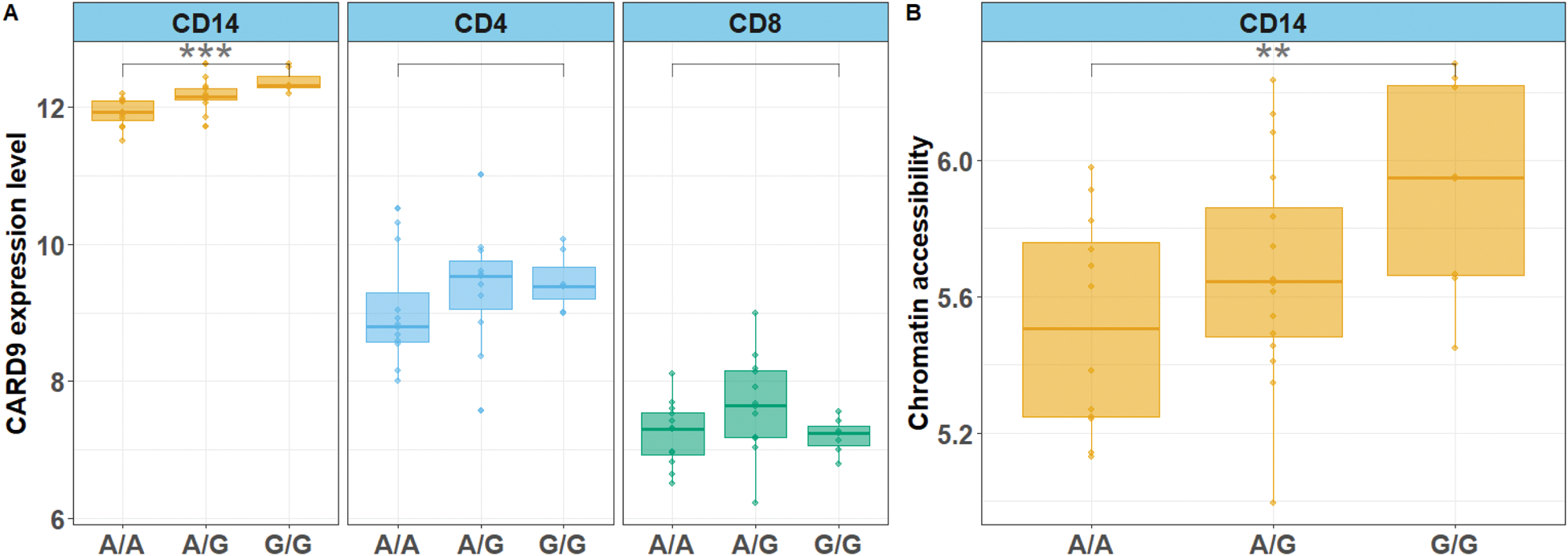
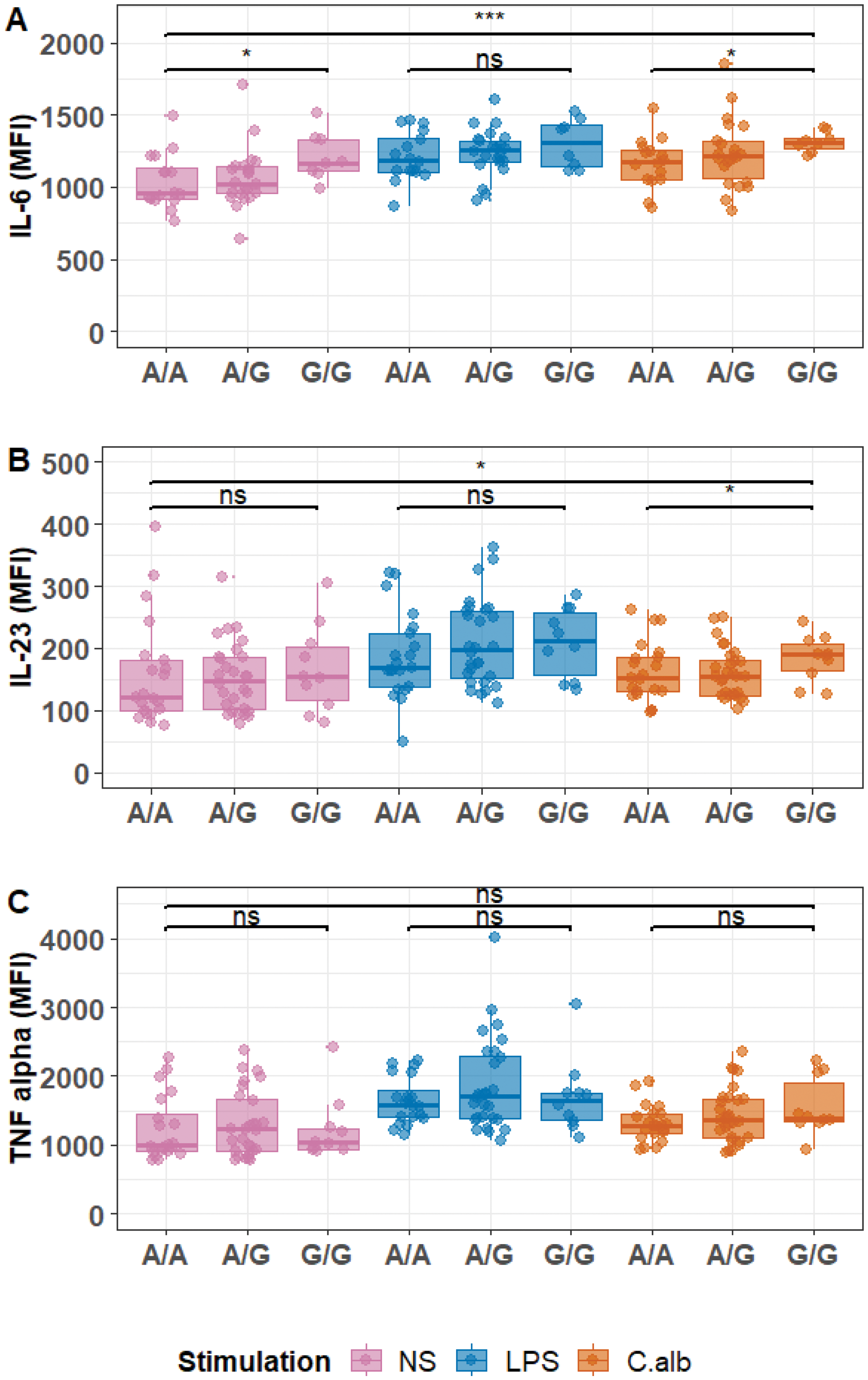
Results: Fine mapping of the CARD9 locus in 4,101 axSpA patients and 9,700 HC prioritized one variant -denoted “SNV CARD9 ”- with a posterior probability exceeding 95% of being causal. This variant is located in an open chromatin region upstream of the CARD9 promoter identified only in monocytes. The axSpA-susceptibility G allele of this SNV was associated with increased CARD9 mRNA expression specifically in CD14+ monocytes and with enhanced chromatin accessibility in its surrounding region (Figure 1). ATACseq footprinting predicted that this SNP would modulate allele-specific binding of the transcription factor ZBTB24 (which is predicted to act upstream of or within hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation) specifically in monocytes. The susceptibility G allele of this SNP was associated with a dose-dependent increase in the production of two key cytokines of the Th17 axis, IL-6 (p-value<0.001) and IL-23 (p-value <0.05), but not with TNFα production (Figure 2).
Conclusion: These results highlight “SNV CARD9 ” as a likely causal variant for the association of the CARD9 locus with axSpA. The variant’s effect in enhancing CARD9 expression and chromatin accessibility in monocytes, coupled with its impact on IL-6 and IL-23 production, underscores its functional relevance for axSpA pathogenesis and the potential therapeutic interest of CARD9 inhibition in carriers of the susceptibility allele.
REFERENCES: [1] International Genetics of Ankylosing Spondylitis Consortium (IGAS), Cortes A, Hadler J, Pointon JP, Robinson PC, Karaderi T, et al. Identification of multiple risk variants for ankylosing spondylitis through high-density genotyping of immune-related loci. Nat Genet 2013;45:730–8.
[2] Brown AC, Cohen CJ, Mielczarek O, Migliorini G, Costantino F, Allcock A, et al. Comprehensive epigenomic profiling reveals the extent of disease-specific chromatin states and informs target discovery in ankylosing spondylitis. Cell Genomics 2023;3:100306.
[3] Bentsen M, Goymann P, Schultheis H, Klee K, Petrova A, Wiegandt R, et al. ATAC-seq footprinting unravels kinetics of transcription factor binding during zygotic genome activation. Nat Commun 2020;11:4267.
[4] Stevens NE, Ryan FJ, Messina NL, Blake SJ, Norton TS, Germano S, et al. No evidence of durable trained immunity after two doses of adenovirus-vectored or mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. J Clin Invest 2023;133:e171742.
CARD9 mRNA expression levels in CD14+ monocytes, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (panel A) and chromatin accessibility of CD14+ monocyte-specific regulatory region upstream of CARD9 promoter (panel B) according to genotype of SNV CARD9 (axSpA-susceptibility allele: G); **: p-value <0.01; *** pvalue <0.001.
Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of IL-6 (panel A), IL-23 (panel B), and TNF alpha (panel C) in monocytes of 59 axSpA patients according to SNV CARD9 genotype in monocytes left unstimulated (“NS”) or after stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or Candida albicans (C.alb). ns: not significant *: p-value <0.05; *** pvalue <0.001.
Acknowledgements: This project was supported by funding from Fondation Bettencourt Schueller, Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM), Foundation for Research in Rheumatology (FOREUM) and Société Française de Rhumatologie (SFR).
Disclosure of Interests: Félicie Costantino Amgen, Celltrion, Jansenn, Lilly, Abbvie, Novartis, UCB, Eva Frison: None declared, Andrew C. Brown Jansenn, Carla Cohen: None declared, Manon Jacoutot: None declared, Gabriele Migliorini: None declared, Roula SAID: None declared, Giuseppe Scozzafava: None declared, Paul Bowness Merck, Benevolent AI, GSK, Regeneron and Novartis. Paul Bryan Wordsworth: None declared, Henri-Jean Garchon: None declared, Simon Glatigny: None declared, Maxime Breban UCB, Novartis, MSD, Novartis, Julian C Knight: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (