

Background: Synovitis in the hand is a hallmark of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Feasible automated systems for synovitis assessment are crucial for future optimal arthritis management. The Arthritis Ultrasound Robot (ARTHUR) is an automated system designed to perform ultrasound scans of hands and wrist joints. Combined with an artificial intelligence (AI) model (DIANA), it can assess and score synovitis.
Objectives: To examine the reliability between robotic ultrasonography (RUS) and standard human ultrasonography (HUS) as performed by an experienced rheumatologist for assessing synovitis in the wrist and finger joints in patients with RA.
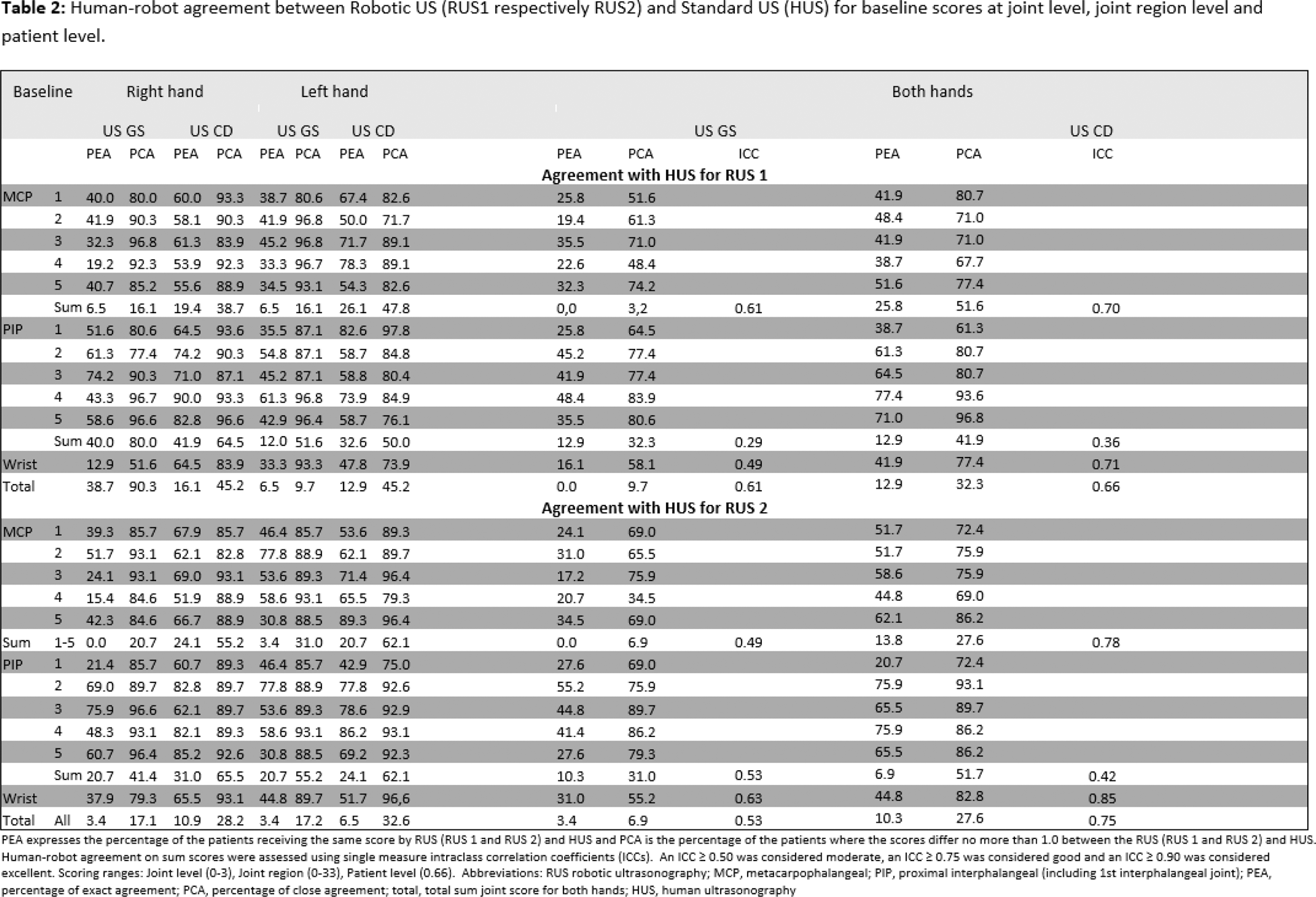
Methods: Twenty-nine RA patients eligible for initiation or intensification of conventional synthetic or biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and with at least one clinically swollen joint in the hand, were included. The ultrasound assessment included the wrists (intercarpal position)), 1st-5th metacarpophalangeal joints (MCPs), 1st interphalangeal joint (IP), and 2nd-4th proximal interphalangeal joints (PIPs) in both hands using RUS and HUS. ARTHUR scanned the patient twice without interval for assessing intra-robot agreement. Synovitis was scored in the standard position from 0-3 for Grey Scale (GS) and Colour Doppler (CD) using the OMERACT-EULAR Synovitis Scoring system. The RUS images obtained by ARTHUR were scored by the DIANA AI software model. The HUS images were scored by one experienced reader, with previously high intra- and inter-reader agreement for the scoring system (quadratic weighted Kappa; 0.88-0.95). The sum score range was 0-66. Disease Activity Score-28 (DAS28), 28 swollen joint count (SJC), 28 tender joint count (TJC) and 22 SJC-hand (corresponding to the hand joints assessed by ultrasound) were assessed at inclusion. Descriptive statistics and agreement between examinations by RUS1 vs RUS2 (intra-robot agreement) and between RUS (RUS1and RUS2) and HUS (human-robot agreement) for sum scores of all joints were evaluated using the percentage of exact agreement (PEA), the percentage of close agreement (PCA) defined as ±1, and single measure intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs).
Results: Patient level Median (25th percentile; 75th percentile) sum scores (range 0-66) for all joints were for RUS1: GS 18 (13.5;21), CD 7 (5;11); for RUS2: GS 19 (15;21), CD 7 (5;13), and for HUS; GS 10 (7;12.5), CD 5 (3;8) (Table 1). Corresponding values for DAS28, SJC28, TLC28 and SJC22 were 4.3 (3.8;4.8), 4 (2.50;5.5), 6 (3,5;7.5) and 3(2;6), respectively. The intra-robot agreement for ARTHUR, based on GS and CD sum scores, showed a PEA of 10.3% for GS and 13.8% for CD. The PCA values were 37.9% for GS and 27.6% for CD, while the ICC values were 0.65 for GS and 0.86 for CD (Table 1). The human-robot agreement for the sum GS between RUS1 and HUS was as follows: PEA 0%, PCA 9.7%, and ICC 0.59. For RUS2 versus SUS, the values were PEA 3.4%, PCA 6.9%, and ICC 0.54. The corresponding CD values for RUS1 and RUS2 versus HUS were: PEA 12.9% and 10.3%, PCA 32.3% and 27.9%, and ICC 0.64 and 0.75, respectively (Table 2). Joint region level The intra-robot agreement between RUS1 and RUS2 showed a GS (score range: 0–6) PEA between 24% and 62% (mean: 40.5%) and a CD PEA interval of 34.5%–86.2% (mean: 50%), with a corresponding sum score ICC ranging from 28% to 87% (mean: 0.64) (Table 1). The human-robot GS agreement for RUS (RUS1 andRUS2) and HUS was as follows: GS PEA ranged from 16.1% to 48.4% (mean: 29%) for RUS1 and 17.2% to 55.2% (mean: 29.6%) for RUS2, while CD PEA ranged from 38.7% to 77.4% (mean: 52.5%) for RUS1 and 44.8% to 75.9% (mean: 56.1%) for RUS2. The sum GS score ICC ranged from 0.29 to 0.61 (mean: 0.51) for RUS1 and from 0.49 to 0.63 (mean: 0.55) for RUS2, with the overall ICC for CD ranging from 0.36 to 0.85 (mean: 0.65) (Table 2). Joint level The intra-robot agreement for GS (score range 0-3) were between 32.1 and 82.8 (63.5). For intra-robot agreement for GS, the best PEA were seen for MCP2-4 and PIP 2-4 (range 57.1-84%), while IP had den lowest agreement (range 32.1.1-50.0%). For CD, PEA values were similar across most joints, except for PIP4, which had the highest PEA at 86.2%, while MCP4 (35.4%) and IP joints (37.9%) demonstrated the lowest values. PCA values for GS and CD were similar across all joint levels (Table 1). The human-robot agreement for GS was between 15,4 and 77.8 (mean 45.6) and for CD between 42.9 and 90.0 (mean 66.9). Lowest agreement was seen for GS in MCP and wrist joints (range 12.9–51.7%). For CD scores, the PEA values were similar. PCA for CD remained consistently high across all joint region levels (Table 2). Scan time The median (25 th percentile; 75 th percentile) scan time required for one RUS scan was 18 minutes and 50 seconds (16 minutes and 48 seconds; 20 minutes and 38 seconds). The scan time for SUS was 12 minutes and 8 seconds (10 minutes and 49 seconds; 13 minutes and 49 seconds).
Conclusion: This study demonstrates a moderate to good overall correlation between robot and human ultrasonography in assessing synovitis in RA hands. However, at the joint level, low agreement was observed, particularly for MCP joints in both intra-robot agreement and human-robot agreement. Overall, the demonstrated agreement between ARTHUR and an experienced human reader was lower than previously reported between human ultrasonographers [1]. However, robot ultrasound shows potential as an alternative to human US for screening and monitoring RA patients, but further software development is required to enhance the accuracy, before to replacing human US.
REFERENCES: [1] Scoring ultrasound synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: a EULAR-OMERACT ultrasound taskforce-Part 2: reliability and application to multiple joints of a standardised consensus-based scoring system. Terslev L, Naredo E, et al. RMD Open. 2017 Jul 11.

Acknowledgements: To our fantastic project nurses, Anne-Mette, Bettina, and Charlotta, who have made an invaluable contribution.
Disclosure of Interests: Mads Ammitzbøll-Danielsen ROPCA ApS provided Arthur free of charge and supported the study through an unrestricted research grant, without access to the data or involvement in data analysis or, Mikkel Østergaard Abbvie, BMS, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, MEDAC, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, and UCB. Abbvie, BMS, Merck, Novartis and UCB, Ho Pui Lydia Tam: None declared, Lene Terslev Novarits, UCB, Johnson and Johnson and GE Healthcare.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (