

Background: Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and cutaneous LE (CLE) have an increased expression of type I interferon (IFN) regulated genes (an IFN signature), which contribute to the disease process. One mechanism behind this IFN signature is an activation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells by RNA and DNA that trigger TLR7 or TLR9, respectively, which via interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) induce the production of large amount of type I IFN [1, 2]. The potent and selective oral IRAK4-inhibitors zabedosertib (BAY1834845) and BAY1830839 have been shown to block TLR signaling in preclinical models as well as in human challenge models [3]. We therefore asked if these IRAK4 inhibitors could inhibit IFN production in an in vitro SLE model and therefore bear the potential as a treatment for SLE and CLE.
Objectives: To investigate the capacity of the two IRAK4-inhibitors zabedosertib (BAY1834845) and BAY1830839 to inhibit the IFN-α production and several proinflammatory cytokines in an in vitro cell system utilizing RNA-containing immune-complexes. In addition, we asked if the IRAK4 effect is additive to hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), which most patients with SLE receive as standard of care.
Methods: CD14-negative peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMCs) from healthy donors were incubated with immune complexes (IC) consisting of U1snRNP and IgG from SLE patients and varying concentrations of Zabedosertib or BAY1830839 for 20 hours, with or without 400 ng/ml hydroxychloroquine (HCQ). The concentration of HCQ in the cell cultures was comparable to the HCQ concentration in patients with SLE treated with HCQ. IFN-α as well as IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α levels in cell cultures were analyzed by immunoassays.
Results: Both Zabedosertib (BAY1834845) and BAY1830839 suppressed the production of IFN-α in a dose-dependent manner, with BAY1830839 demonstrating a slightly stronger effect (Figure 1). Suppression of the IFN-α synthesis was also observed in the presence of HCQ, but the combination of an IRAK4 inhibitor and HCQ lead to a slightly more prominent suppression. Similar patterns were noted for IL-6 and TNF-α production, whereas IL-8 reduction was marginal and unaffected by HCQ.
Inhibition of RNA-IC induced IFN-α production by two IRAK4 inhibitors and HCQ. CD14-negative PBMC from healthy blood donors were stimulated with RNA-containing immune complexes (RNA-IC), in presence of different concentrations of IRAK4 inhibitors (A) BAY1830839 or (B) BAY1834845 with or without HCQ (400 ng/ml). IFN-α was measured in the cell culture supernatants at 20h by a DELFIA immunoassay. The results are shown as mean values of seven donors ± SEM of seven donors.
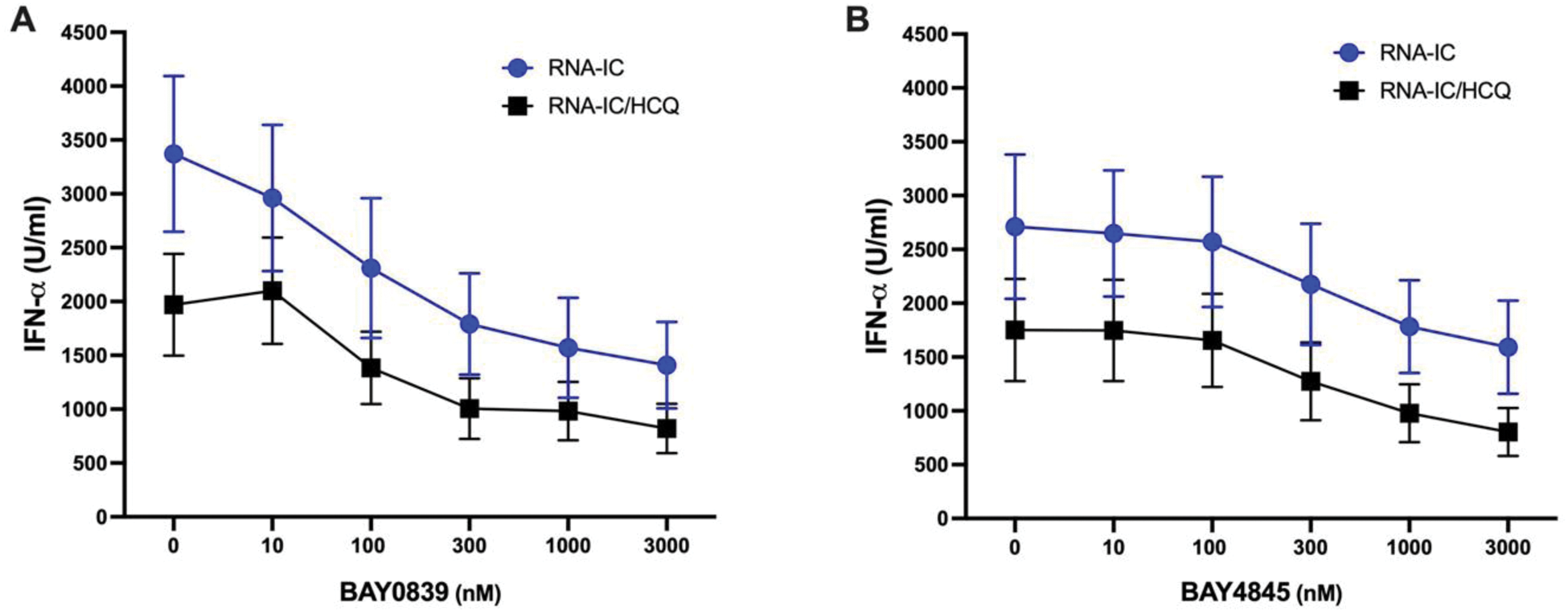
Conclusion: Both IRAK4 inhibitors investigated in the present study efficiently suppressed the IFN-a production in an in vitro SLE model system. Moreover, both drugs enhanced the pharmacological effect of HCQ. BAY1830839 and BAY1834845 should therefore be further explored as therapeutic options for oral treatment of patients with SLE and CLE.
REFERENCES: [1] Rönnblom L, Leonard D. Interferon pathway in SLE: one key to unlocking the mystery of the disease. Lupus Science & Medicine 2019;6:e000270. doi:10.1136/lupus-2018-000270.
[2] Herrada AA, Escobedo N, Iruretagoyena M, Valenzuela RA, Burgos PI, Cuitino L, et al. Innate immune cells’ contribution to systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2019;10:772.
[3] Jodl SJ, Ten Voorde W, Klein S, Wagenfeld A, Zollmann FS, Feldmüller M, Klarenbeek NB, de Bruin DT, Jansen MAA, Rissmann R, Rohde B, Moerland M. The oral IRAK4 inhibitors zabedosertib and BAY1830839 suppress local and systemic immune responses in a randomized trial in healthy male volunteers. Clin Transl Sci. 2024 Mar;17(3):e13771. doi: 10.1111/cts.13771. PMID: 38511583; PMCID: PMC10955609.
Acknowledgements: Beside Bayer the study was supported by grants from the Swedish Rheumatism Association, the King Gustav V’s 80-year Foundation, and the Swedish Society of Medicine and the Ingegerd Johansson donation.
Disclosure of Interests: Stefan Jodl Bayer, Sanofi, Bayer, Sanofi, Raphael Dahmen Sanofi, Bayer, Sanofi, Andrea Wagenfeld Bayer, Maija-leena Eloranta: None declared, Lars Ronnblom Astra-Zeneca, Biogen.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (