

Background: Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy has emerged as a promising treatment option for patients with systemic autoimmune diseases that are resistant to conventional therapies [1]. Its efficacy is believed to stem from their ability to eliminate B cells in tissues. Recent findings have demonstrated that anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy effectively eliminates B cells within the lymph nodes of patients with systemic autoimmune diseases [2], however the impact on the bone marrow remains to be determined.
Objectives: To investigate the effect of anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy in the bone marrow of patients with systemic autoimmune diseases.
Methods: Three patients with severe, treatment-resistant systemic autoimmune diseases (Table 1) received autologous anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy following conditioning therapy with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide [3, 4]. Bone marrow biopsies were performed prior to therapy (Patients 2 and 3) and after therapy (Patient 1 and 2 at week 16, and Patient 3 at week 7). Immune phenotyping of B and T cells was conducted via flow cytometry.
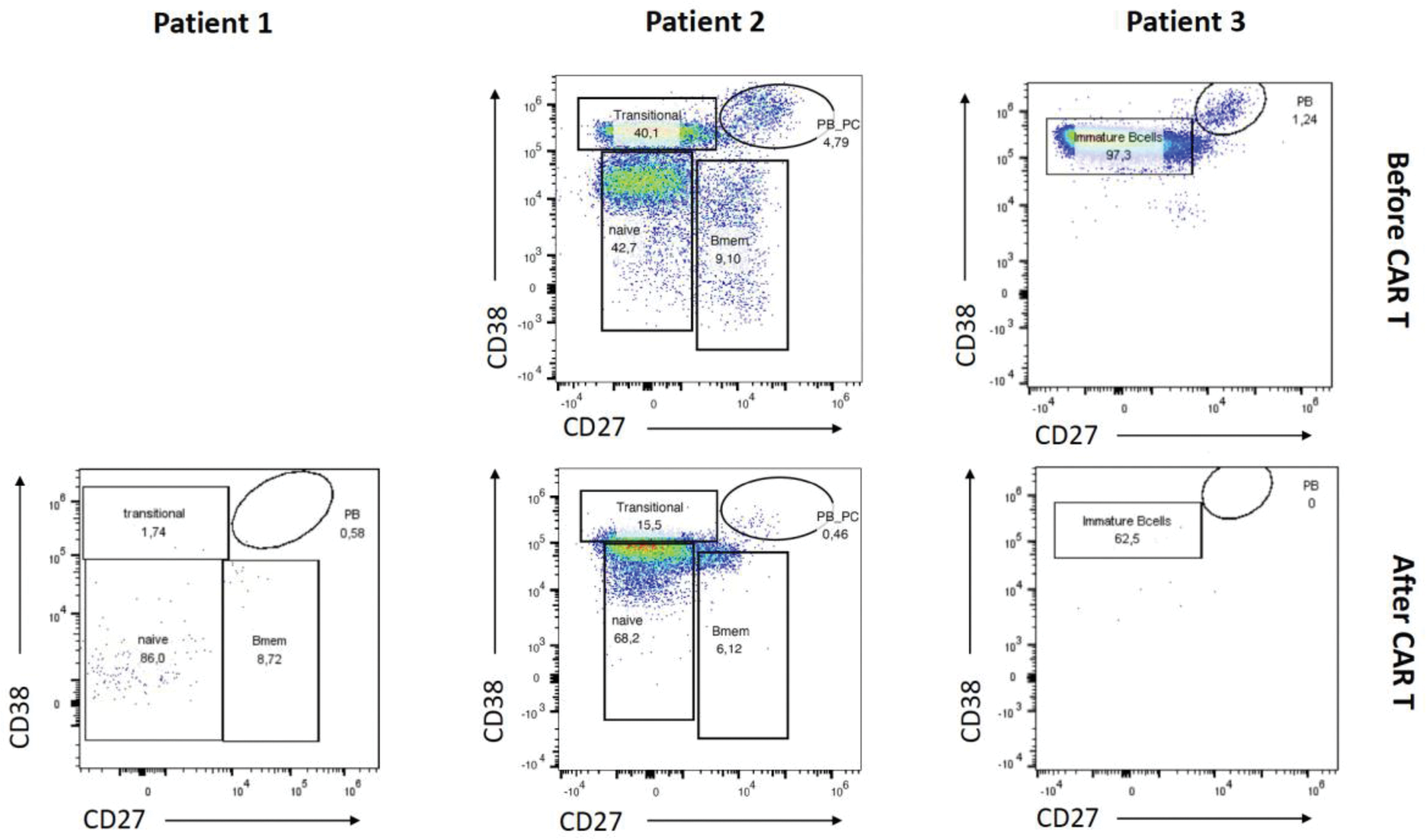
Results: Treatment with KYV-101 appeared to be safe (Table 1). Stable clinical improvement was achieved following anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy, even after discontinuation of all other immunosuppressive treatments. Bone marrow biopsies were performed on two patients (Patients 1 and 3) prior to peripheral B cell reconstitution. In these patients, B cells, particularly CD19+ plasmablasts and CD19+ plasma cells, were significantly reduced at weeks 16 and 7, respectively (Figure 1). In contrast, the bone marrow biopsy in patient 2 was conducted after B cell reconstitution. At week 16, post-anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy and following B cell reconstitution, B cells in the bone marrow of patient 2 predominantly exhibited a naive/transitional phenotype, suggesting the re-emergence of naive/transitional B cells (Figure 1). Additionally, memory B cells were decreased, and CD19+ plasmablasts and plasma cells were notably diminished (Figure 1).
Conclusion: This study highlights that anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy, combined with standard lymphodepleting regimens, promotes remission in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases by fully depleting B cells within primary lymphatic organs.
REFERENCES: [1] Müller F et al. N Engl J Med 2024.
[2] Tur C et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2024.
[3] Minopoulou I et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2025.
[4] Albach F et al. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2025.
Patient characteristics.
| Characteristic | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disease | SLE | Overlap Syndrome of SSc with RA | PR3+ AAV |
| Age | 46 | 32 | 52 |
| Sex | Male | Female | Male |
| Previous immunosuppressive
| glucocorticoids,
| glucocorticoids, methotrexate, azathioprine,
| glucocorticoids,
|
| Safety and tolerability | CRS= Grade 1
| CRS= Grade 2
| CRS= Grade 1
|
| Disease activity before anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy | SLEDAI-2K=14 | mRSS=9
| BVAS=2
|
| Disease activity after anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy | SLEDAI-2K=4
| mRSS=3
| BVAS=0
|
BVAS, Birmingham vasculitis activity score; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; CRS, cytokine release syndrome; DAS28-CRP, disease activity score for rheumatoid arthritis with CRP; DLCO, diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide; FVC, forced vital capacity; ICANS, immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity; mRSS, modified Rodnan skin score; PR3+ AAV, proteinase 3+ ANCA-associated vasculitis; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SLEDAI-2K, systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000; SSc, systemic sclerosis; VDI, vasculitis damage index.
Dot plots showing FACS analysis of B cells from the bone marrow before (Patient 2 and 3) and after (Patient 1, 2 and 3) anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy stained with anti-CD38 and anti-CD27.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Ioanna Minopoulou AbbVie, Novartis, Lilly, Artur Wilhelm: None declared, Fredrik N. Albach: None declared, Arnd Kleyer: None declared, Edgar Wiebe: None declared, Anja Fleischmann: None declared, Mareike Frick: None declared, Frederik Damm: None declared, Dominic Borie Kyverna Therapeutics, Vincent Casteleyn: None declared, Robert Biesen: None declared, Thomas Dörner AbelZeta, BMS, J&J, Novartis, Roche/Genentech, Tobias Alexander: None declared, Jan Zernicke: None declared, Lukas Hinkelmann: None declared, Elpida Phitak: None declared, Norman Michael Drzeniek: None declared, Kamran Movassaghi: None declared, Marie Luise Hütter-Krönke: None declared, Eva Schrezenmeier: None declared, Adrian Schreiber: None declared, Udo Schneider: None declared, Georg Schett: None declared, Lars Bullinger: None declared, Gerhard Krönke: None declared, Olaf Penack Alexion, Gilead, Jazz, MSD, Neovii, Novartis, Pfizer and Therakos, David Simon AbbVie, Alfasigma, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen-Cilag, Lilly, Novartis, UCB.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (