

Background: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is associated with metabolic comorbidities, including obesity, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension. Metabolic comorbidities induce chronic inflammation, increase cardiovascular disease risk, and may be associated with increased PsA disease activity. However, only a few studies have explored the impact of these comorbidities on treatment outcomes in PsA.
Objectives: We investigated the association between metabolic comorbidities and the 12-month retention rate of a first-line biologic/targeted synthetic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug (b/tsDMARD) in patients with PsA treated in routine care.
Methods: Patients with PsA who initiated their first b/tsDMARD after 2014 were identified in 10 registries participating in the European Spondyloarthritis Research Collaboration Network (EuroSpA) that were able to register the following four metabolic comorbidities: obesity, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension at b/tsDMARD treatment start (baseline). The comorbidity status in each patient was calculated (0 (reference) versus ≥1). Co-existence between comorbidities was displayed in a Venn diagram. Kaplan-Meier estimation with log-rank tests and Cox regression with hazard ratios (HR), adjusting for baseline age, sex, purchasing power-adjusted Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita per €1,000 [1], and calendar year, were applied to assess and compare 12-month drug retention rates between patients with 0 vs ≥1 comorbidities.
Results: Of the 8,162 included patients, 36% (n=2,912) had at least one metabolic comorbidity. Compared with patients with no metabolic comorbidity, patients with comorbidity were older, more often treated with an interleukin 17 inhibitor as first b/tsDMARD and had higher scores for disease activity and patient-reported outcomes, Table 1. Among the 2,912 patients, a considerable overlap between the metabolic comorbidities was observed, and 40% (n=1,147) had two or more comorbidities, Figure 1. The 12-month crude retention rate for patients with no metabolic comorbidity was 78% versus 77% for patients with ≥1 metabolic comorbidity. The risk of treatment withdrawal was higher in patients with ≥1 metabolic comorbidity (HR 1.12 [95% confidence interval 1.03-1.22] compared to no metabolic comorbidity in the adjusted analyses.
Baseline characteristics in patients with PsA having 0 or ≥1 metabolic comorbidities (obesity, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension).
| No metabolic comorbidity
| Data availability | ≥1 metabolic comorbidity
| Data availability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 53 (44, 61) | 100% | 60 (52, 67) | 100% |
| Sex, female | 51% | 100% | 54% | 100% |
| BMI, kg/m 2 | 26 (23, 28) | 77% | 31 (28, 35) | 93% |
| Time since diagnosis, years | 9 (5, 13) | 89% | 9 (6, 14) | 97% |
| Obesity, BMI≥30 | 0 (0%) | 96% | 1,673 (58%) | 99% |
| Diabetes* | 0 (0%) | 100% | 520 (15%) | 100% |
| Dyslipidemia | 0 (0%) | 100% | 611 (21%) | 100% |
| Hypertension | 0 (0%) | 100% | 1,684 (58%) | 100% |
| 28 swollen joint count | 2 (0, 5) | 75% | 4 (1, 7) | 89% |
| 28 tender joint count | 3 (1, 8) | 75% | 6 (2, 11) | 89% |
| CRP, mg/l | 4 (1, 12) | 77% | 7 (2, 17) | 89% |
| PGA, 0-10 | 6 (4, 8) | 63% | 7 (5, 8) | 57% |
| DAPSA28, 0-75 | 20 (14, 32) | 40% | 26 (17, 40) | 38% |
| HAQ, 0-3 | 0.75 (0.25, 1.25) | 52% | 1.25 (0.75, 1.63) | 63% |
| TNFi/IL17i/JAKi/Other | 77%/13%/2%/8% | 100% | 72%/18%/1%/8% | 100% |
Data are as observed, median (25%, 75% percentiles) unless otherwise stated. Pooled data from 10 registries: ATTRA (Czech Republic), ERSBTR (Estonia), ROBFIN (Finland), RABBIT-SpA (Germany), NOR-DMARD (Norway), Reuma.pt (Portugal), RRBR (Romania), BioRx.si (Slovenia), BIOBADASER (Spain), and SCQM (Switzerland).
Patients with missing registration on a comorbidity were classified as not having the comorbidity.
*Diabetes registration differed across registries and was defined based on information on type 1 diabetes mellitus, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and undifferentiated diabetes.
Abbreviations: BMI, Body Mass Index; CRP, C-reactive protein; DAPSA28, Disease Activity index for PSoriatic Arthritis in 28 joints; HAQ, Health Assessment Questionnaire; IL17i, interleukin 17 inhibitor; JAKi, Janus kinase inhibitor; N, number of patients in the cohort; PGA, Patient Global Assessment; TNFi, Tumor Necrosis Factor inhibitor.
Venn diagram illustrating the distribution of metabolic comorbidities and overlap thereof in the 2,912 PsA patients who had at least one comorbidity.
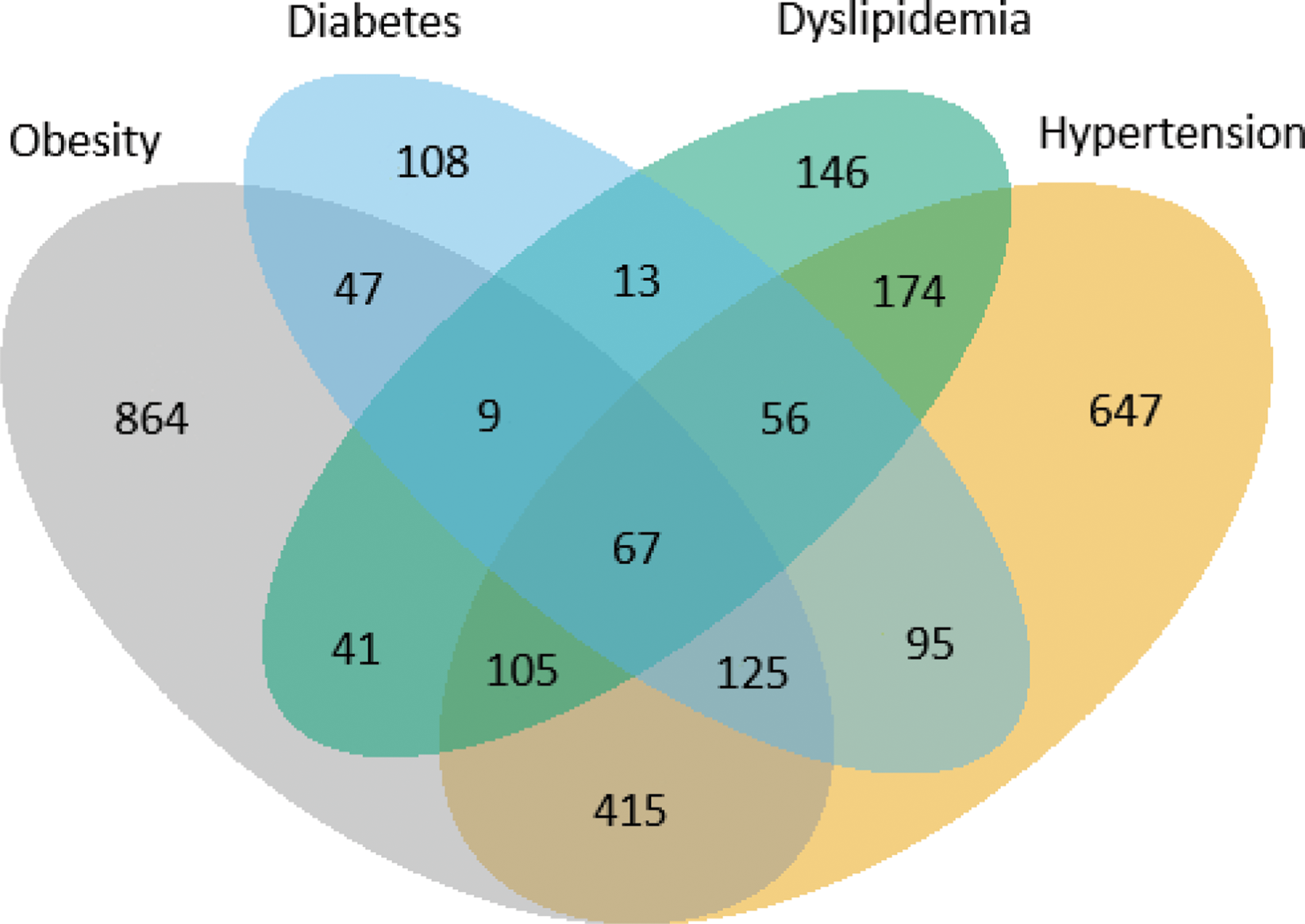
Conclusion: In patients with PsA, metabolic comorbidities were prevalent and often overlapping. Patients with one or more metabolic comorbidity had higher disease activity at treatment start, and a slightly higher risk of treatment withdrawal within the first 12 months compared to patients without any metabolic comorbidity. The clinical implications of our findings need to be further investigated.
REFERENCES: [1] European Union.
Acknowledgements: The EuroSpA collaboration has been supported by Novartis Pharma AG since 2017 and UCB Biopharma SRL since 2022. No financial sponsors had any influence on the data collection, statistical analyses, abstract preparation, or decision to submit.
Disclosure of Interests: Zohra Faizy Ahmadzay Research grant from Novartis (payed to the employer), Lykke Midtbøll Ørnbjerg Research grant from Novartis (paid to the employer), Mikkel Østergaard Abbvie, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Hospira, Janssen, MEDAC, Merck, Novartis, Novo, Orion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi and UCB, Abbvie, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Hospira, Janssen, MEDAC, Merck, Novartis, Novo, Orion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi and UCB, AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Merck, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and UCB, Jacob Jørgensen Research grant from Novartis (payed to the employer), Jette Heberg Research grant from Novartis and UCB, Anne Gitte Loft Novartis, UCB, Janssen, Novartis, UCB, Brigitte Michelsen Speaker’s fees from Novartis, Research grant from Novartis (paid to employer). Centre for treatment of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases (REMEDY) is funded as a Centre for Clinical Treatment Research by The Research Council of Norway (project 328657), Gareth T. Jones Janssen, UCB, Research grants (paid to employer) from AbbVie, Pfizer, UCB, Amgen, GSK, Menarini and Shionogi, Pasoon Hellamand Research grant from Novartis (paid to employer), Signe Møller-Bisgaard Research grant AbbVie, Kasper Yde Jensen Research grant from Novo Nordic Foundation (payed to the employer), Mehrdad Shoae Kazemi Payed to employer from Novartis and UCB, Parham Karimi Reikandeh: None declared, Jakub Závada Abbvie, Elli-Lilly, Sandoz, Novartis, Egis, UCB, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Sobi, Abbvie, Swix-biopharma, Glaxo, Miguel Bernardes Advisory board and/or speaker fees from AbbVie, Janssen, GSK, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Advisory board and/or speaker fees from AbbVie, Janssen, GSK, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Elsa Vieira-Sousa Speaker fees from Novartis, Abbvie, MSD, Celgene, UCB, Research grants from MSD, Pfizer, UCB, Isabel Castrejon SBMS, Boehringer, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gebro, GSK, Janssen, Pfizer, UCB, Consultant for Alfasigma, Pfizer, UCB, Lucía Otero-Varela: None declared, Catalin Codreanu AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ewopharma, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, Sobi, AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sobi, Laura Kuusalo Abbvie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Galapagos, Eli Lilly, Medac, Pfizer, UCB, Galapagos, Pfizer, Lilly, Johnson & Johnson, UCB, Vappu Rantalaiho Abbvie, BMS, Novartis, Viatris, Johnson&Johnson, Lilly, Anne Regierer Amgen, BMS, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, RABBIT-SpA is supported by a joint, unconditional grant from AbbVie, Amgen, Biocon, Biogen, Celltrion, Hexal, Janssen-Cilag, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Andreas Reich RABBIT-SpA is supported by a joint, unconditional grant from AbbVie, Amgen, Biocon, Biogen, Celltrion, Hexal, Janssen-Cilag, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Burkhard Moeller Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Amgen, Raphael Micheroli Abbvie, Janssen, UCB, Tore K. Kvien Grünenthal, Sandoz, and UCB, AbbVie, Amgen, Celltrion, Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, UCB, Galapagos, AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Galapagos, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB (to the institution), Sella Aarrestad Provan Boehringer Ingelheim, Boehringer Ingelheim, Karin Laas Abbvie, Johnson and Johnson, Novartis, Pfizer, Sigrid Vorobjov: None declared, Ziga Rotar Abbvie, Amgen, Novartis, MSD, Medis, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi, Lek, Janssen, Abbvie, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Janssen, Sobi, Swixx BioPharma, AstraZeneca, Katja Perdan-Pirkmajer Abbvie, Novartis, MSD, Medis, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Lek, Abbvie, Novartis, Medis, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Florenzo Iannone consulting and/or speaking from Abbvie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Galapagos, Janssen, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, consulting and/or speaking from Abbvie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Galapagos, Janssen, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Research grant from BMS, Galapagos, Pfizer, Fabrizio Conti AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, UCB, Astrazeneca, GSK, Bjorn Gudbjornsson: None declared, Daniela Di Giuseppe: None declared, Marleen G.H. van de Sande Speakers fee: Novartis, UCB, Janssen, Eli Lily, Consultant for Novartis, Abbvie, Eli Lilly, UCB, Grant/research support: UCB, Janssen, Novartis, Handan Yarkan-Tuğsal: None declared, Merete Lund Hetland Speaker for Pfizer, Medac, Sandoz (no personal income, institution); speaker for Novartis (personal income), Advisory Board Abbvie (No personal income, paid to institution). Prev. chaired the steering committee of the Danish Rheumatology Quality Registry (DANBIO, DRQ), which receives public funding from the hospital owners and funding from pharmaceutical companies, Research grants (institution) from Abbvie, Biogen, BMS, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Janssen Biologics B.V, Lundbeck Fonden, MSD, Medac, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Biopies, Sandoz, Novartis, Nordforsk, Bente Glintborg Research grants from Pfizer, Abbvie, BMS, Sandoz.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (