

Background: In the osteoarthritis (OA) pathophysiology, synovial macrophages play diverse and significant roles. M1 macrophages, also known as proinflammatory macrophages are distinguished by their production of a series of inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). In contrast, M2 macrophages showed anti-inflammatory functions in the OA [1]. A latest study had shown that, as an important messenger molecule, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) can act on the EP2 (PTGER2) receptor of macrophages, promoting senescent macrophages to secrete inflammatory mediators and mediating the local inflammatory microenvironment [2]. However, the roles and mechanisms of PGE2 in the development of osteoarthritis (OA) remain unclear.
Objectives: To investigate the roles and regulatory mechanisms of PGE2 in synovial macrophages and their polarisation in the development of OA.
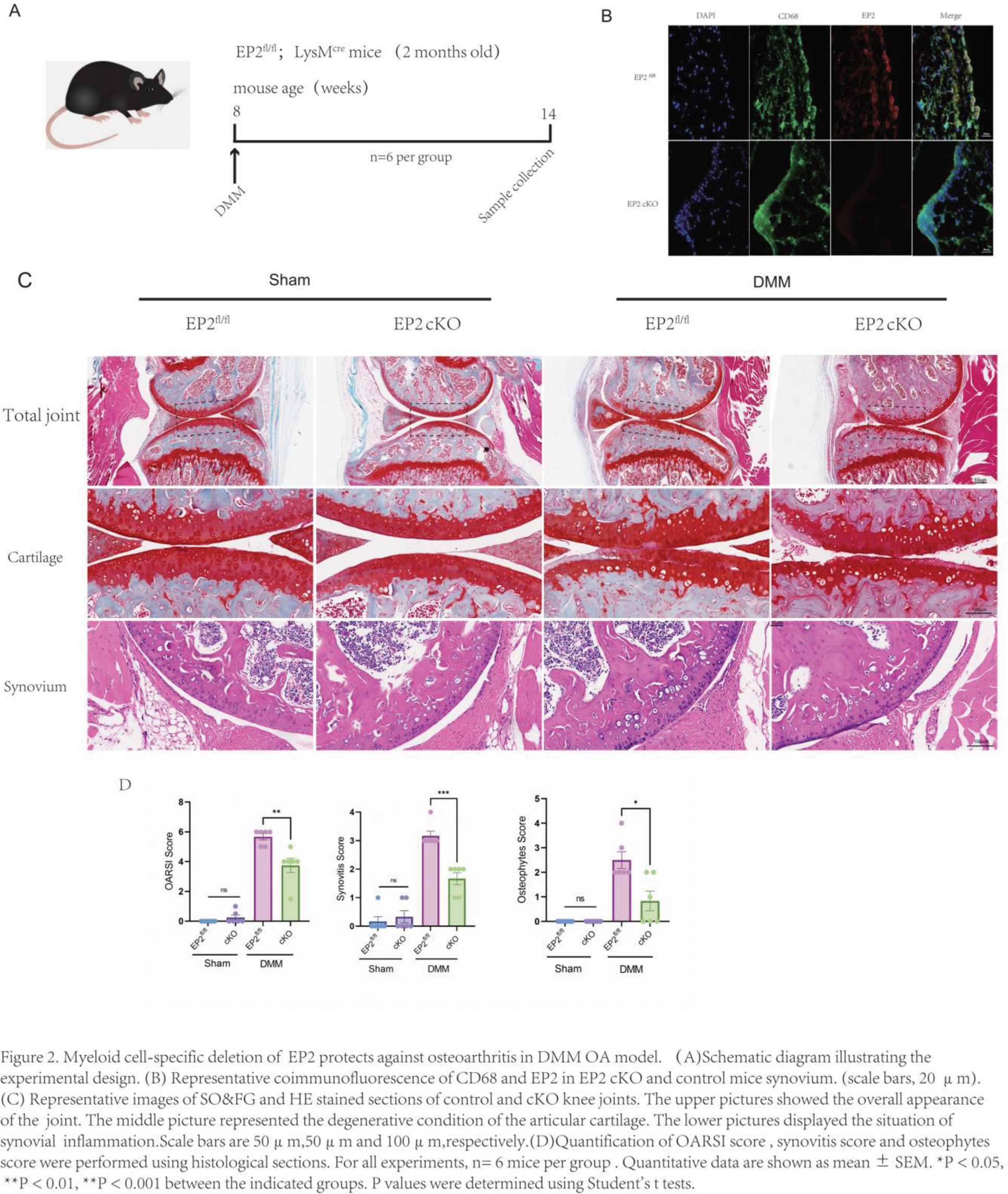
Methods: Synovial tissues and blood sample from normal patients and patients with OA were collected.Young and aged mice were given intra-articular injection of PGE2 after DMM surgery.Mice with EP2 deletion specifically in the myeloid lineage were generated and subjected to intra-articular injection of collagenase (collagenase induced osteoarthritis, CIOA) and destabilisation of the medial meniscus (DMM) surgery to induce OA.Cartilage damage and synovitis were measured by Osteoarthritis Research Society International score and synovitis score system. Additionally, we isolated mouse BMDM cells, pretreated them with IL-4 to induce M2 polarization, and then treated them with PGE2 with or without EP2 inhibitor (PF-04418948) to investigate the role of PGE2-EP2 signal in vitro. The mRNA of BMDM cells were extracted and RNA-sequence analysis were performed.
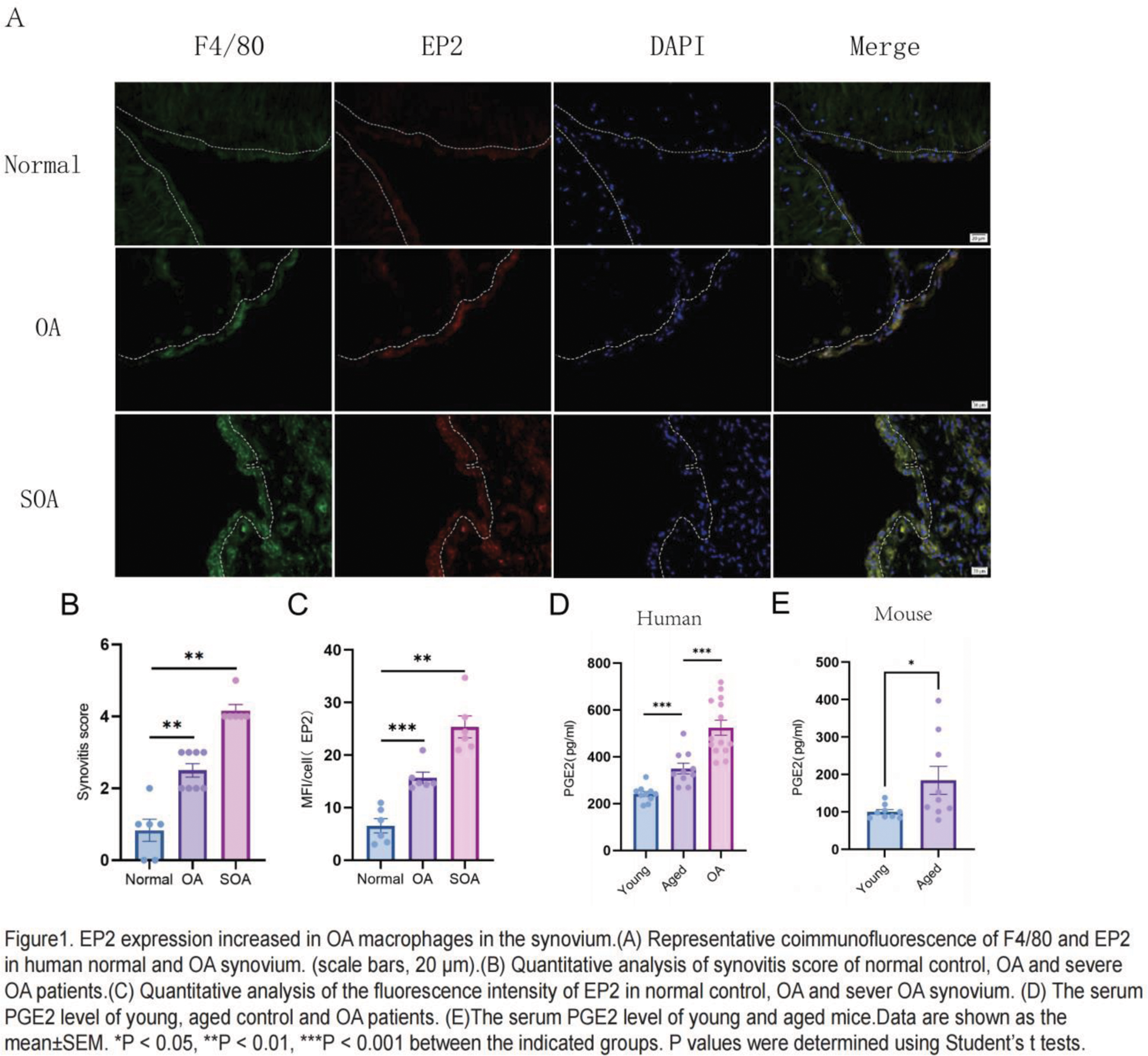
Results: We found the expression of EP2 is significantly upregulated in synovial macrophages of human osteoarthritis and was associated with the severity of synovitis. The levels of serum prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in patients with OA and elderly patients are higher than those in normal individuals. Intra-articular injection of PGE2 after DMM surgery can exacerbate the progression of osteoarthritis (OA) in both young or aged mice. PGE2 treatment can convert anti-inflammatory macrophages into a pro-inflammatory phenotype. RNA-sequence analysis suggested Hif-1α as an important transcription factor, is involved in the regulation of macrophages by PGE2. And Hif-1α inhibitor(PX-478) treatment can reverse the pro-inflammatory effect of PGE2 on M2 macrophages. Compared with the littermate control mice, myeloid specific conditional EP2 knockout (cKO) mice showed decreased M1 macrophage polarization and attenuated severity of synovitis, an elevated expression of cartilage phenotype protein collagen II (COL2), and a decreased expression of cartilage degradation markers matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP-13) in OA cartilage.
Conclusion: PGE2-EP2 signal reprogrammed proinflammatory macrophages through a Hif-1α-dependent NF-kB activation manner.
REFERENCES: [1] Sanchez-Lopez E, Coras R, Torres A, Lane NE, Guma M. Synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis progression. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022. 18(5): 258-275.
[2] Minhas PS, Latif-Hernandez A, McReynolds MR, et al. Restoring metabolism of myeloid cells reverses cognitive decline in ageing. Nature. 2021. 590(7844): 122-128.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (