

Background: Methotrexate (MTX) is a cornerstone treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), used by most patients starting therapy. However, 30–40% of patients fail to achieve satisfactory disease control, necessitating alternative or advanced therapies. Early and effective treatment is critical, as response to initial therapy can influence long-term outcomes. While clinical factors such as sex, seropositivity, and disability scores moderately predict MTX efficacy, they lack sufficient accuracy and fail to capture biological pathways. Genomic and transcriptomic biomarkers offer promise but are often limited by single-timepoint assessments This study leverages comprehensive whole-blood RNA sequencing data to identify predictive biomarker profiles for MTX response using machine learning.
Objectives: To identify blood-based transcriptomics biomarkers of MTX response in patients with early RA.
Methods: Whole blood samples were taken from patients taking part in the Rheumatoid Arthritis Medication Study (RAMS), an observational longitudinal cohort of early RA patients starting MTX for the first time in the UK. RNA-seq data was generated using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform of patients before and after 4-weeks MTX treatment. Treatment response was determined after 6 months on drug and patients were classified as responders (with good and moderate responders grouped together) or non-responders using established EULAR response criteria. Differential gene expression analysis was performed using glmmSeq [1], which uses generalized linear mixed model with negative binomial distribution. Models were parameterized with size factor and dispersion estimated using DESeq2 [2]. The regression model included patient ID as a random effect and an interaction term was included between time-point and response category. All linear mixed models were adjusted for baseline disease activity (DAS28). Enrichment analysis for differentially expressed genes was performed using Metascape [3]. A machine learning pipeline was employed to classify MTX response using the baseline transcript data as input. The pipeline involved feature selection with the aforementioned linear-model, followed by gradient boosted tree ensemble model (XGBoost) under 10-fold cross validation. Model performance was assessed using area under the receiver operator characteristic (ROC-AUC) curve.
Patient Characteristics of early RA patients participating in the study. DAS28—CRP: Disease activity score in 28 joints with C-reactive protein; csDMARD: conventional synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; HAQ Score: health assessment questionnaire score; BMI: body mass index; Disease Duration measured in years.
| Grouped by Response | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | No | Yes | ||
| Characteristic | n=100 | n=31 | n=69 | |
| Sex, n (% ) | Female | 79 (79.0 ) | 28 (90.3 ) | 51 (73.9 ) |
| Concurrent csDMARD usage, n (% ) | Yes | 23 (23.0 ) | 9 (29.0 ) | 14 (20.3 ) |
| Age, mean (SD ) | 59.9 (12.4 ) | 58.3 (12.5 ) | 60.6 (12.3 ) | |
| DAS28 -CRP , mean (SD ) | 4.7 (1.0 ) | 4.4 (0.9 ) | 4.8 (1.0 ) | |
| HAQ Score, mean (SD ) | 1.4 (0.7 ) | 1.5 (0.8 ) | 1.3 (0.7 ) | |
| BMI, mean (SD ) | 29.4 (6.5 ) | 30.5 (6.7 ) | 28.9 (6.4 ) | |
| Disease Duration, median [Q1,Q3] | 0.3 [0.2,1.3] | 0.4 [0.2,2.4] | 0.3 [0.2,1.1] | |
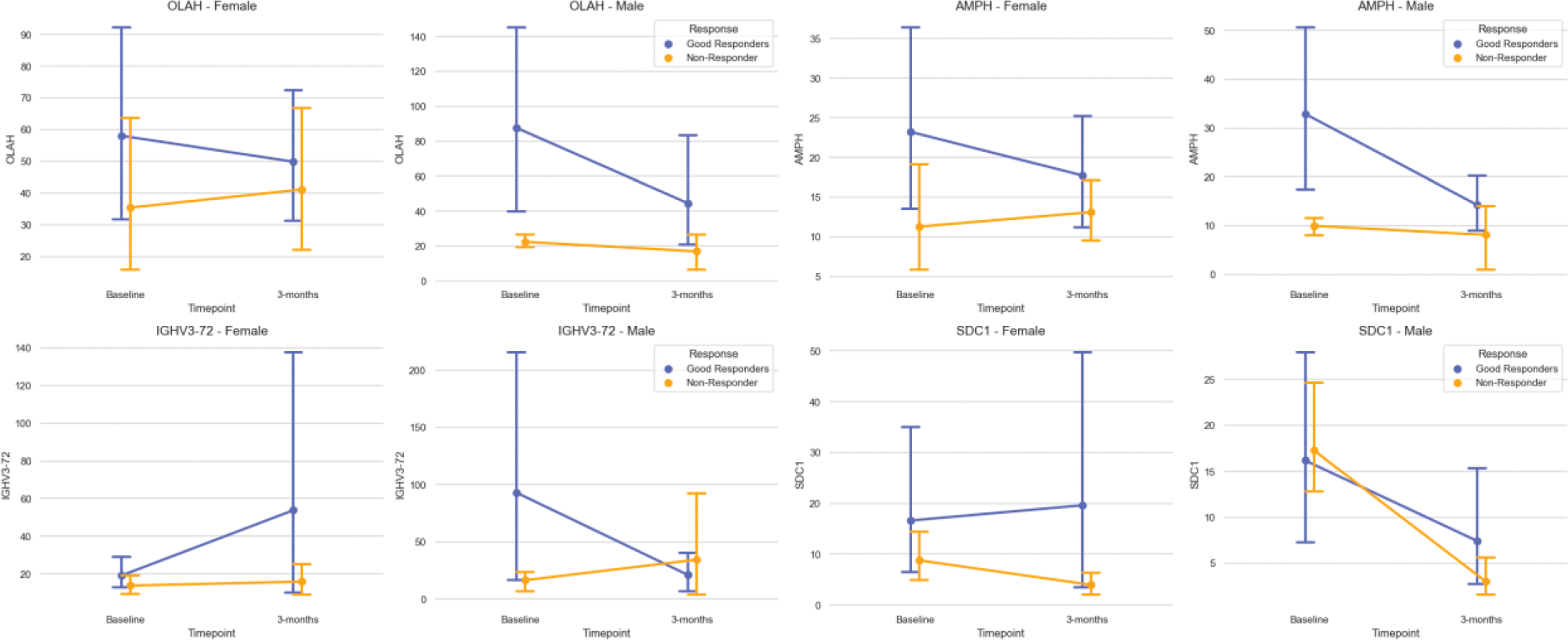
Following data quality control 16,548 genes were available for analysis in 100 patients. Patients were either categorised as responders (n=69) or non-responders (n=31) following 6-months of MTX therapy. The baseline characteristics of the patients are presented in Table 1. Ninety-three genes were identified as differentially expressed between responders and non-responders across both timepoints. Eighty-one of these were not statistically significant in the interaction term, that is they were not dependent on time. Arachidonate 15-Lipoxygenase, Oleoyl-ACP Hydrolase ( OLAH ) was upregulated in good-responders with fold changes (FC) of 1.56, and its expression was impacted by timepoint, where responder’s gene expression was reduced by 0.76 FC over the 4 weeks (Figure 1). This pattern of expression was also observed for IGHV3-72 and Amphiphysin (AMPH), with reduced in expression in responders by 0.76 and 0.68, respectively, (Figure 1). Syndecan 1 (SDC1) was found to be upregulated in responders (1.23 FC) and this was dependent on time with upregulation after 4-weeks. The machine learning pipeline achieved a mean ROC-AUC of 0.89 ± 0.07. Results from the linear mixed model and machine learning model were subject to enrichment analyis seperately; however, as expected, both had overlap in immune related pathways, which was unsurprising considering the autoimmune nature of the disease.
Normalised gene count plot with standard error for genes with statistically significant interaction between response and timepoint. Plots are stratified by sex.
Conclusion: In conclusion, this study provides valuable insights into the molecular underpinnings of MTX response in RA. The high classification performance observed provides a basis for future biomarker research aimed at improving personalized treatment strategies, but will require replication in independent data sets. The study’s novel approach and significant findings contribute to the growing body of knowledge in RA treatment and precision medicine.
REFERENCES: [1] Myles Lewis KG, Elisabetta Sciacca, Cankut Cubuk, Anna Surace. glmmSeq: General Linear Mixed Models for Gene-level Differential Expression 2021 [Available from:
[2] Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 2014;15(12):550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8.
[3] Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, et al. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun 2019;10(1):1523. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09234-6 [published Online First: 20190403]
Acknowledgements: 3TR Consortium.
Disclosure of Interests: Chuan Fu Yap: None declared, Nisha Nair: None declared, S. Verstappen BMS and AbbVie research grants, Kimme Hyrich: None declared, Anne Barton: None declared, Darren Plant: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (