

Background Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a rare connective tissue disease characterized by autoimmunity, vasculopathy, and fibrosis involving many organs. To date, the gastrointestinal (GI) involvement accounts for few therapeutic options, while cutaneous and vascular manifestations are often refractory to standard treatments. Immunoglobulin (Ig) therapy is an interesting option as it exhibits both immunomodulatory and antifibrotic properties even though its efficacy on GI, skin and muscle involvement has been described only in case series with limited numbers of patients.
Objectives To evaluate the efficacy of Ig therapy on GI, cutaneous, and vascular involvement in SSc.
Methods a retrospective observational study was conducted evaluating SSc patients treated with Ig at a 2 gr/kg/month dosage either intravenously (IV) or subcutaneously (SC). Demographical data, antibodies positivity, associated therapies (vasoactive and immunosuppressants) and disease duration were collected. Moreover, the presence of diarrhea, gastroesophageal reflux (GER), dysphagia, digital edema, digital ulcers (DUs), as well as the modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS) and videocapillaroscopic pattern (VCP: normal, early, active, late) were assessed at baseline (BL) and after 6 (T6) and 12 (T12) months of Ig therapy. Variation of these items from BL to T6 and T12 was tested by Paired T Test, Mc Nemar test, Wilcoxon’s signed rank test as appropriate. Regression analyses were than performed to assess influence of possible confounders variables (vasoactive and immunosuppressants drugs) on outcome variables (VCP, digital edema, DUs).
Results Clinical records of 65 patients were analyzed. Mean age was 56.18 (± 12.32 SD) and median disease duration was 10.00 years (min-max 1.00-38.00). Sixty-three patients (96.9%) were ANA positive, with positivity for anti-centromeric antibodies in 23 (35.4%), SCL-70 in 27 (41.5%) and RNA polymerase III in 8 (12.3%) patients. Ig were administrated IV in 57 patients and SC in 8 patients. Table 1 summarized the trend of clinical items from BL to T12.
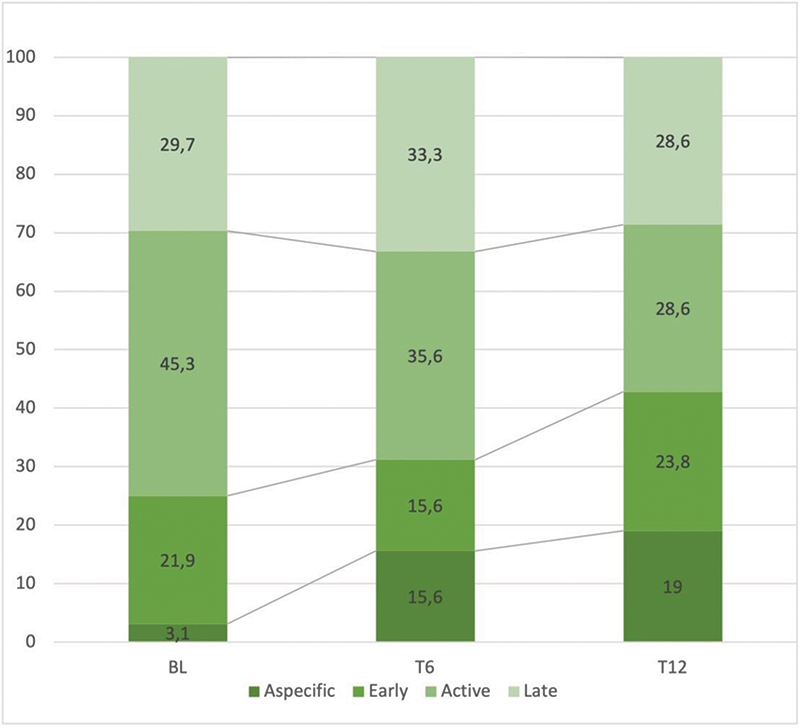
At BL, 49.2% of patients complained diarrhea, 90.8% GER, 51.6% dysphagia, 76.9% digital edema; 38.5% presented DUs. VCP was normal in 3.1% of patients, early in 21.9%, active in 45.3%, and late in 29.7%. Also, median mRSS was 10 (min-max 0-50).
At T6, median mRSS significatively improved [6 (min-max 0-34), p<0.0000001] together with VCP (normal in 15.6%, early in 15.6%, active in 35.6%, and late in 33.3%, p=0.00448). Moreover, a significative reduction of the prevalence of GER (49.2%, p<0.000001), diarrhea (19.4%, p<0.0001), dysphagia (22%, p<0.0001), digital edema (44.4%, p<0.0001), DUs (14.1%, p=0.0022) was noted.
At T12, median MRSS improved even more [3 (min-max 0-23), p<0.00000001] along with VCP (normal in 19.0%, early in 23.8%, active in 28.6%, and late in 28.6%, p=0.00596). Also, the prevalence of GER was lower (25.9%, p<0.001). Regression analyses did not evidence any influence of other treatments on the tested outcome variables.
Conclusion Our data confirms literature data on Ig therapy efficacy towards GI and skin manifestations [1]. To date, this is the first study presenting a possible positive effect on the vascular component shown by the improvement in VCP; these data should be confirmed with prospective randomized studies on bigger samples.
Reference [1]Agostini, E. et al. Autoimm Rev 20, 102981 (2021).
| BL | T6 | P value (BL-T6) | T12 | P value (T6-T12) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GER, n (%) | 59 (90.8) | 31 (49.2) | p<0.000001 | 15 (25.9) | p<0.001 |
| Dysphagia, n (%) | 32 (51.6) | 13 (22) | p<0.0001 | 6 (10.7) | 0.0736 |
| Diarrhea, n (%) | 31 (49.2) | 12 (19.4) | p<0.0001 | 4 (6.9) | 0.0771 |
| mRSS, median (min-max) | 10 (0-50) | 6 (0-34) | p<0.0000001 | 3 (0-23) | p<0.00000001 |
| Digital edema, n (%) | 50 (76.9) | 28 (44.4) | p<0.0001 | 17 (30.9) | 0.131 |
| Digital ulcers, n (%) | 25 (38.5) | 9 (14.1) | 0.0022 | 3 (5.3) | 0.0736 |
| VCP, n |
64 |
45 |
0.00448 | 42 |
0.00596 |
Figure 1.
Image/graph:
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests None Declared.
Keywords: Skin, Gastrointestinal tract, Systemic sclerosis
DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2023-eular.2987