

Background: Spondyloarthritis(SpA) is chronic inflammatory disease affecting the axial skeleton and enthesis. Recent studies have highlighted the role of Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of SpA. However, Innate immune mechanisms preceded to Th17 cells activation and interaction of monocytes with CD4 + T cells in SpA are not well known.
Objectives: The aim of this study is to investigate the role of allograft inflammatory factor 1 (AIF-1) which is primarily expressed in activated monocytes in the pathogenesis of SpA, especially on Th17 cells polarization.
Methods: CD14 + monocytes were isolated from human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (hPBMC)s using CD14 MicroBeads. CD4 + T cells were isolated by CD4 + T cell Isolation Kit. CD14 + monocytes were stimulated for 24 h and CD4 + T cells for 72 h with 100 ng/mL of recombinant human AIF-1. RNA sequencing was performed to compare the whole transcriptomes of AIF-1-stimulated cells to control(vehicle)- stimulated groups. Cytokines were measured in the stimulated supernatant using ELISA kits. Upregulation of AIF-1 gene was confirmed by qRT-PCR. AIF-1 siRNA (20 nM) or scrambled siRNA (20 nM) was transfected into monocytes for 6 h.
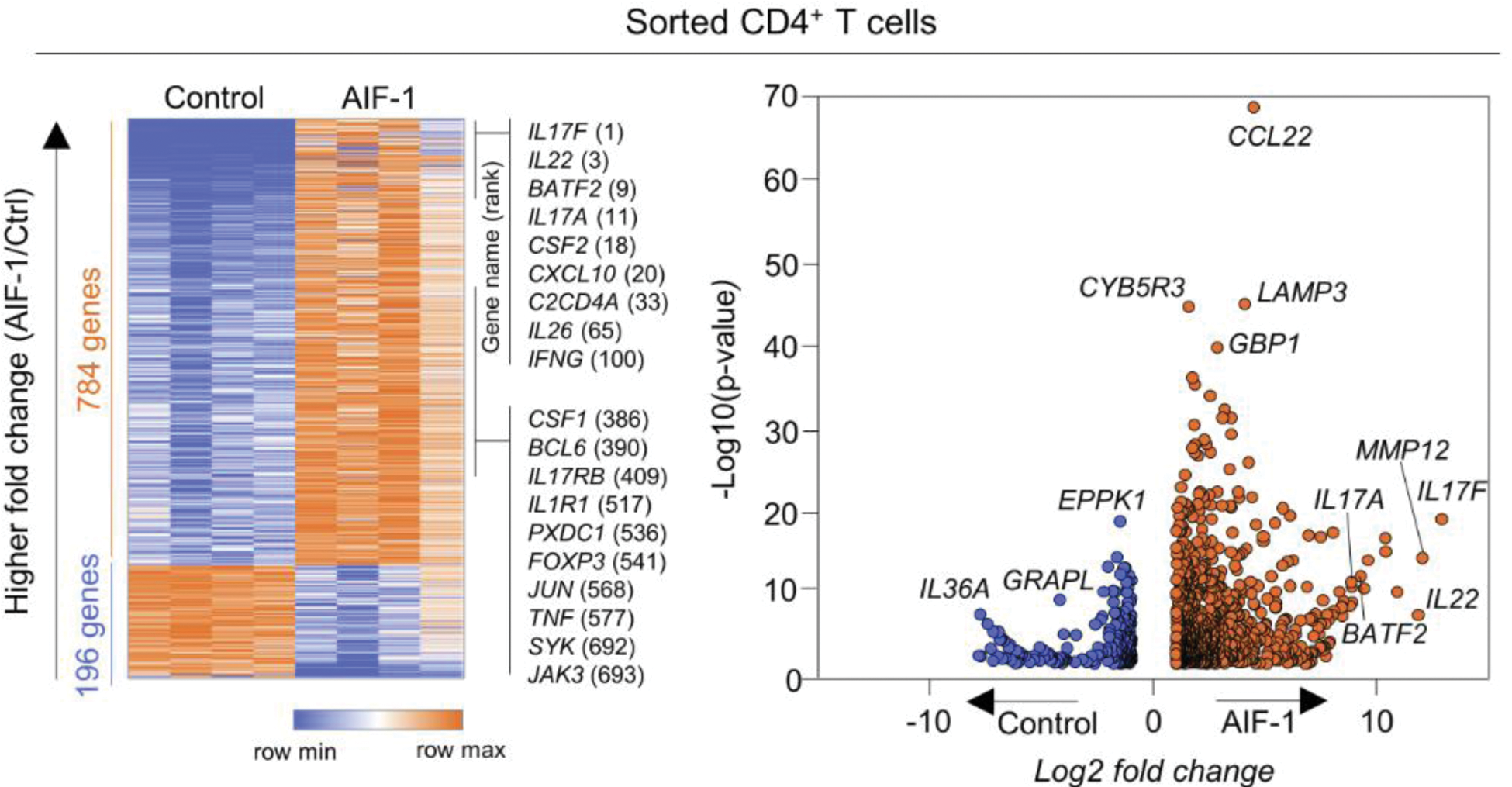
Results: Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ, IFN-α and TNF-α increased AIF-1 gene expression in monocytes. Monocytes with high expression of AIF-1 exhibit classical monocyte features. AIF-1 treatment stimulates CD14 + monocytes to produce Th17-driving cytokines. In vitro stimulation of AIF-1 directly drove CD4 + T cells toward a pro-inflammatory Th17 cells and Th1 cells fate. AIF-1-treated CD4 + T cells exhibit metabolic features of Th17 cells. In monocytes and CD4 + T cells Co-culture, AIF-1 elevated monocytes polarized CD4 + T cells into Th17 cells, but when AIF-1 was knocked down, polarization was reduced.
Conclusion: AIF-1 is able to polarize CD4 + T cells toward Th17 cells via not only a direct effect on CD4 + T cells, but also indirect mechanisms by which CD14 + monocytes producing Th17-driving cytokines. Activated monocytes represented by high AIF-1 may be an important player in the pathogenesis of SpA.
REFERENCES: [1] Diego, et al. AIF1: Function and Connection with Inflammatory Diseases. Biology (Basel). 2023 May 9;12(5):694.
[2] Elizondo, D.M., et al., Allograft inflammatory factor 1 in myeloid cells drives autoimmunity in type I Diabetes. JCI Insight, 2020. 5.(10).
[3] Zheng,Y., et al., TNFα promotes Th17 cell differentiation through IL-6 and IL-1β produced by monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol Res, 2014: p. 385352.
Among DEGs upregulated in AIF-1 stimulated CD4 + T cells, the expression of Th17- associated cytokine genes, such as IL17F, IL22, IL17A and IL26 was increased.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (