

Background: Risankizumab (RZB), an interleukin-23 inhibitor, has demonstrated efficacy and safety for the treatment of PsA in two phase 3 clinical trials [1, 2]. However, there is limited real-world evidence available regarding patient outcomes for PsA patients early in their disease course following treatment with RZB.
Objectives: To evaluate the real-world effectiveness and patient/physician satisfaction with RZB for the treatment of biologic-naïve patients with early PsA (diagnosed ≤ 24 months) in routine clinical practice across the United States (US) and Europe.
Methods: In this retrospective analysis (June 2023 to June 2024) using data from the Adelphi Spondyloarthritis VI Disease Specific Programme™, biologic-naïve patients with early PsA receiving RZB 150 mg (subcutaneous injection) were included from the US and Europe (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom). The analysis was based on cross-sectional questionnaires completed by physicians (assessing effectiveness and satisfaction) and their consulting patients (assessing satisfaction) during their most recent visits. Effectiveness assessments included change in the proportion of patients with dactylitis or enthesitis, mean change in TJC68, SJC66, and physician assessments of pain and fatigue (rated on a 0 to 10 scale, with higher scores indicating worse outcomes) from treatment initiation to the most recent visit using McNemar or t tests ( P <.05). In addition, the proportions of patients achieving clinically meaningful improvements, including complete resolution of dactylitis and enthesitis, TJC68 and SJC66 (equal to 0 or ≤ 1 among patients with scores > 1 at treatment initiation), and minimal clinically important difference in pain (≥ 1.0-unit decrease) and fatigue (≥ 3.0-unit decrease), were assessed. Data collected from patient and physician surveys were used to evaluate satisfaction with disease control following RZB treatment. Outcomes were evaluated in biologic-naïve ± conventional synthetic (cs)DMARD patients with early PsA (overall patient population) and in the following subgroups: (1) patients naïve to biologics with an inadequate response to ≥ 1 csDMARD (biologic-naïve + csDMARD-IR) and (2) patients naïve to both biologics and csDMARDs (biologic-naïve + csDMARD-naïve).
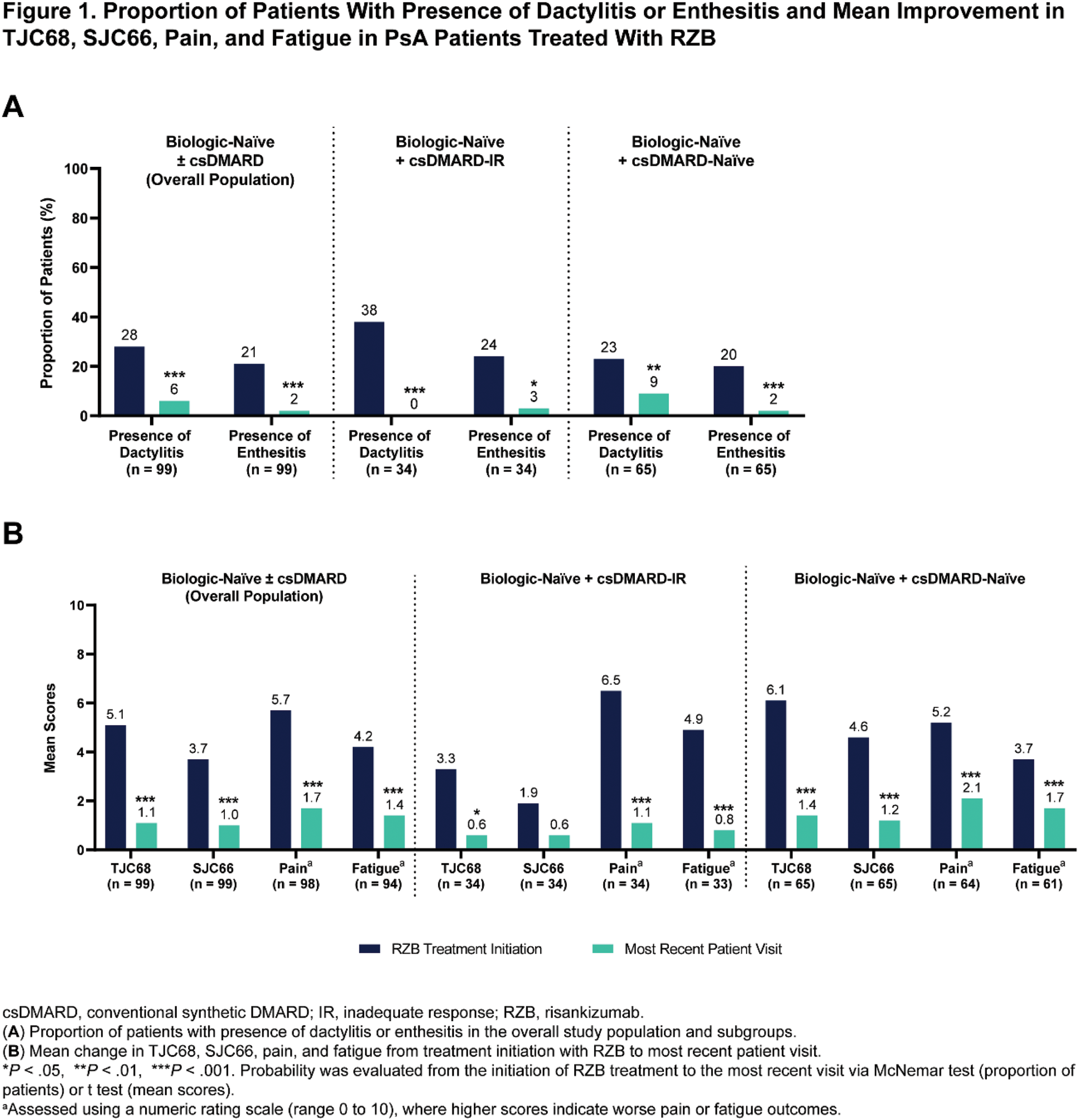
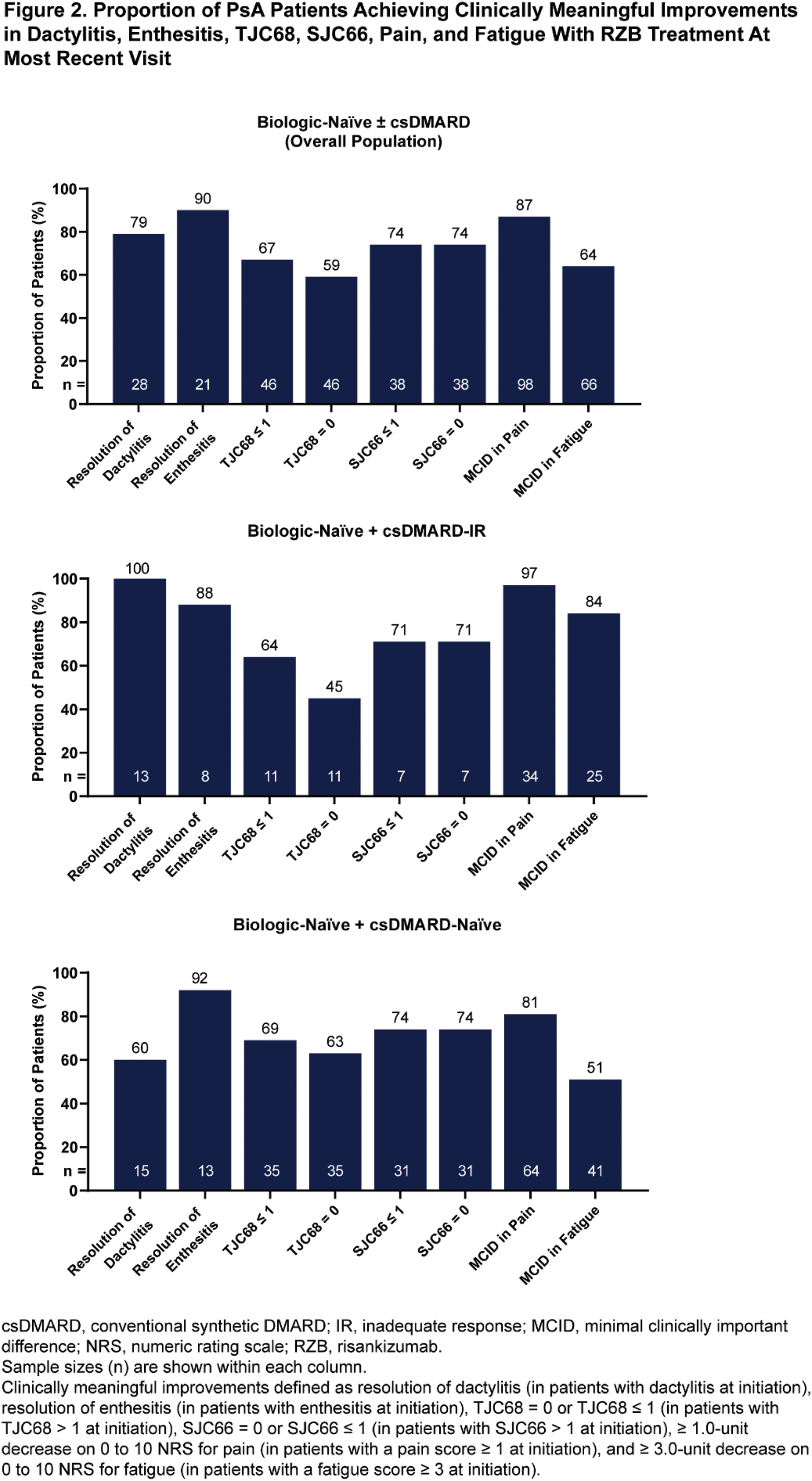
Results: A total of 99 patients who initiated treatment with RZB were included in the analysis, with 55 (56%) from the US and 44 (44%) from Europe. Patients were on average 43.1 years old at the time of data collection, 47% were female, and body surface area affected by psoriasis was 12.9% at treatment initiation. The mean duration of RZB treatment was 9.1 months, and the mean TJC68 and SJC66 at treatment initiation was 5.1 and 3.7, respectively. Baseline characteristics were generally similar across subgroups. Significant improvements in the presence of dactylitis and enthesitis and mean change in TJC68, SJC66, pain, and fatigue were observed from treatment initiation to the most recent visit (all comparisons, P ≤.001) (Figure 1). High rates of complete resolution of dactylitis (79%) and enthesitis (90%), TJC68 ≤ 1 (67%) and SJC66 ≤ 1 (74%), and achievement of clinically meaningful improvements in pain (87%) and fatigue (64%) were observed. Effectiveness results in the biologic-naïve + csDMARD-IR subgroup were generally similar to those observed in the overall population, except for mean change in SJC66 (Figures 1-2). Improvements were also noted in the biologic-naïve + csDMARD-naïve subgroup, although certain endpoints (such as resolution of dactylitis and fatigue) appeared less pronounced compared to the overall population. Patient- and physician-reported satisfaction (n = 17 and n = 99, respectively) on the ability of RZB to control disease was 88% and 97% in the overall population.
Conclusion: In real-world clinical settings, biologic-naïve patients with early PsA who initiated RZB treatment demonstrated significant and clinically meaningful improvements in peripheral joint involvement, pain, and fatigue. Both patients and physicians reported high levels of satisfaction with RZB as an effective treatment for disease control in biologic-naïve PsA.
REFERENCES: [1] Kristensen LE, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81:225-31.
[2] Östör A, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81:351-58.
Acknowledgements: Data collection was undertaken by Adelphi Real World as part of an independent survey, entitled the Spondyloarthritis (SpA) VI Disease Specific Programme (DSP™). The DSP is a wholly owned Adelphi product and is the intellectual property of Adelphi Real World. The analysis described here used data from the Adelphi SpA VI DSP. AbbVie was one of multiple subscribers to the DSP and did not influence the original survey through either contribution to the design of questionnaires or data collection. All authors had access to the data results and participated in the development, review, and approval of this publication. No honoraria or payments were made for authorship. Medical writing support was provided by Matthew Eckwahl, PhD of AbbVie.
Disclosure of Interests: Jessica A. Walsh has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB Pharma, research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB Pharma, William Tillett received speaker fees from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Ono, Pfizer, and UCB, consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Ono, Pfizer, and UCB, research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, and UCB, Christopher D Saffore may hold stock or stock options from AbbVie, employee of AbbVie, Xiaolan Ye may hold stock or stock options from AbbVie, employee of AbbVie, Manish Patel may hold stock or stock options from AbbVie, employee of AbbVie, Ana Biljan may hold stock or stock options from AbbVie, employee of AbbVie, Jamie Vora may hold stock or stock options from AbbVie, employee of AbbVie, Isabel Truman employee of Adelphi Real World, consultant to AbbVie for this analysis, Molly Edwards employee of Adelphi Real World, consultant to AbbVie for this analysis, Gary Milligan employee of Adelphi Real World, consultant to AbbVie for this analysis, Andrew Ostor served as a consultant and/or on advisory boards for AbbVie, GSK, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer, grant/research support from AbbVie, GSK, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (