

Background: Sonelokimab is a novel IL-17A- and IL-17F-inhibiting Nanobody that is designed to target difficult-to-reach sites of inflammation due to its small size and albumin-binding domain. The randomized, placebo-controlled Phase 2 ARGO trial in patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) demonstrated the efficacy of sonelokimab on both joint and skin outcomes [1]. Notably, sonelokimab treatment also resulted in robust multidomain clinical responses that have previously been associated with improved quality of life (QoL).
Objectives: Assess the effect of sonelokimab on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in the Phase 2 ARGO trial in patients with active PsA.
Methods: ARGO (NCT05640245) was a 24-week, global, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled adult patients with a confirmed diagnosis of active PsA [1]. Patients were randomized to sonelokimab 120mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) with induction (induction doses at Weeks 0, 2, 4, and 6), sonelokimab 60 mg Q4W with induction, sonelokimab 60 mg Q4W with no induction (NI), placebo, or adalimumab 40 mg every 2 weeks (reference arm). The first 12 weeks of the study were placebo controlled, after which patients originally randomized to placebo switched to sonelokimab 120 mg NI. PROs including PsA Impact of Disease (PsAID)-12 (score range 0–10), Patient’s Assessment of Arthritis Pain (PtAAP; score range 0–100), Patient’s Global Assessment of Disease Activity (PGA; score range 0–100), and Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI; score range 0–3) were assessed Q4W until Week 24. Statistical comparisons vs. placebo were conducted at Week 12 using a mixed model for repeated measures analysis. No statistical comparisons were performed for the adalimumab reference arm (not powered for comparisons).
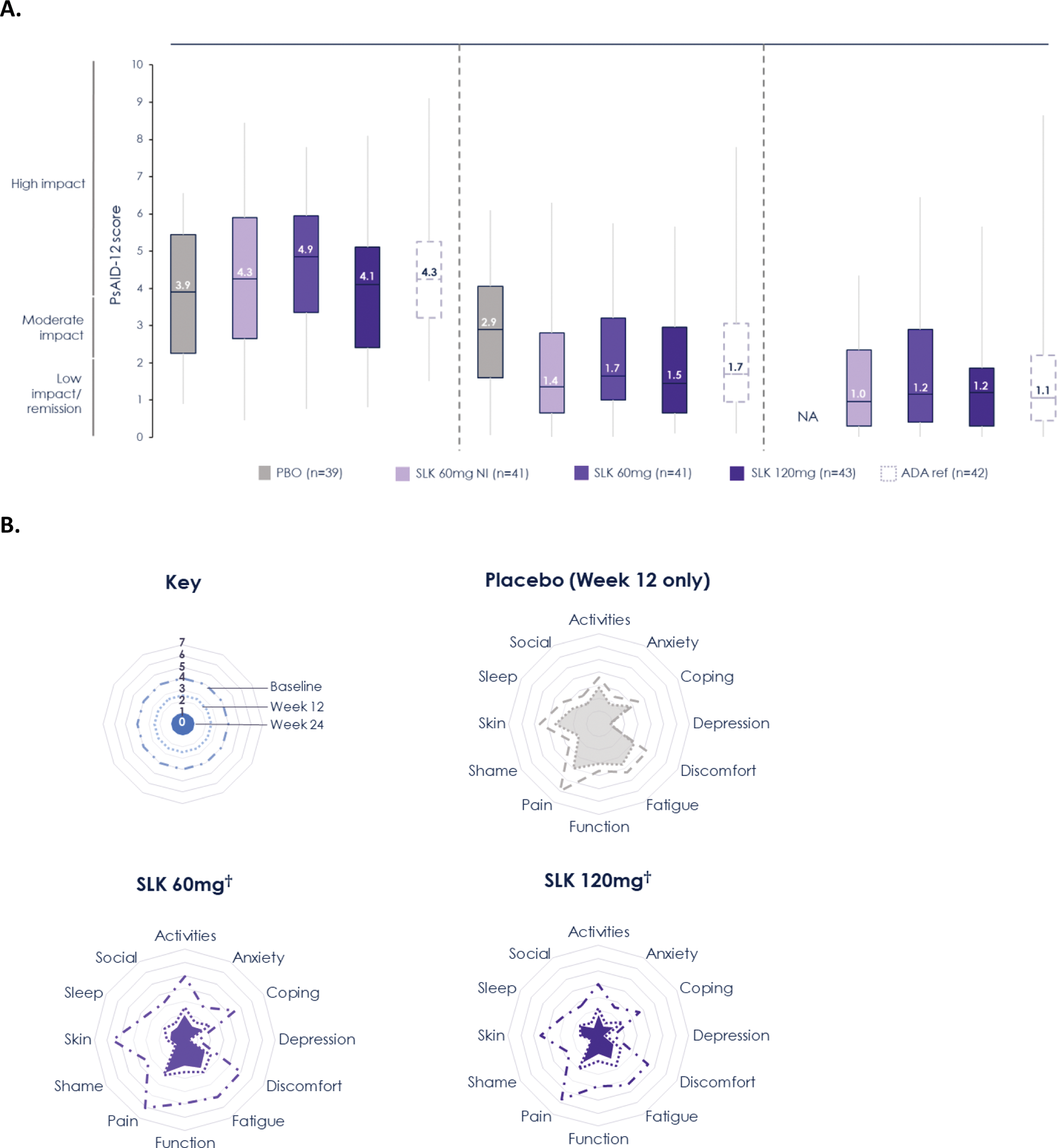
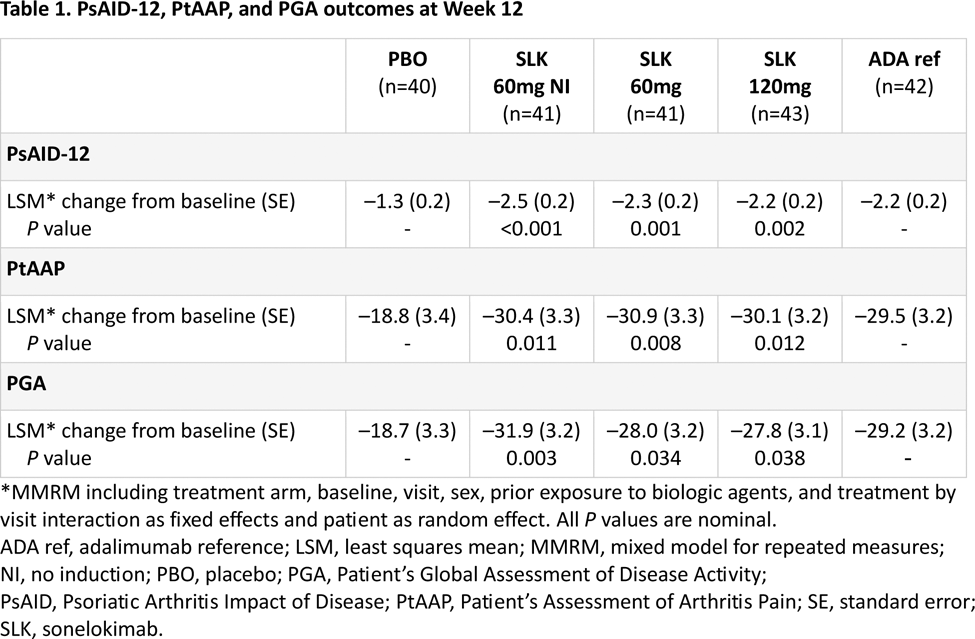
Results: Overall, 207 participants were randomized. Patient-reported PsA symptom burden was relatively high at baseline (median PsAID-12 total scores: 3.9–4.9; Figure 1A). Sonelokimab treatment resulted in significant improvements in PsAID-12 scores at Week 12, with overall reductions of 2.2–2.5 vs. 1.3 points with placebo (Table 1) and benefits across almost all individual domains (Figure 1B). Continued sonelokimab treatment resulted in further improvements over time, with most patients achieving PsAID-12 low impact/remission by Week 24 (median score: 1.0–1.2; Figure 1A). Improvements in PsAID-12 were pronounced in patients who achieved both clinical joint and skin response (ACR50 + PASI 100), with a median score of 0.5 at Week 24 across sonelokimab arms (mean [SD] improvement from baseline of –3.0 [1.9] points). Significant improvements in pain by Week 12 were also observed with sonelokimab, with decreases in PtAAP scores of 29.5–30.9 vs. 18.8 points with placebo (Table 1). These improvements continued to Week 24, with a mean change from baseline of –36.2 [–64.2%] to –40.0 [–65.6%] points with sonelokimab. Similarly, significant improvements in patient-reported disease activity by Week 12 were observed with sonelokimab, with decreases in PGA scores of 27.8–31.9 vs. 18.7 points with placebo (Table 1). These improvements also continued to Week 24, with a mean change from baseline ranging from –32.7 (–52.1%) to –39.7 (–35.6%) points with sonelokimab. HAQ-DI scores improved from baseline through Week 24 (mean change from baseline at Week 24 of 0.47 [–47.4%] to 0.60 [–59.1%] points with sonelokimab), although improvements did not reach statistical significance vs. placebo at Week 12.
Conclusion: Patients treated with sonelokimab in ARGO reported significant improvements in the symptoms and impact of PsA. Phase 3 studies (IZAR-1: NCT06641076 and IZAR-2: NCT06641089) will further characterize the effect of sonelokimab on PROs and QoL in a larger patient population.
REFERENCES: [1] McInnes et al . Efficacy and safety of sonelokimab, a novel IL-17A- and IL-17F-inhibiting Nanobody ® , in patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA): Results from the global, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 2 ARGO trial. EULAR 2024 (Presentation OP0195).
(A) Change from baseline in PsAID-12 total score through Week 24* and (B) response across individual PsAID-12 items through Week 24. *Data show median (horizontal line), interquartile range (box), and minimum/maximum (whiskers). LOCF from Week 12 to 24 has been applied to patients who either switched treatment arm due to lack of response at Week 12 or completed the study at Week 12. All other missing data were imputed using LOCF. A score of ≤1.15 denotes remission/no symptoms/no impact, >1.15–1.95 denotes low symptom/impact severity, >1.95–3.60 denotes moderate symptom/impact severity, and >3.6 denotes high symptom/impact severity. †With induction doses.ADA ref, adalimumab reference; LOCF, last observation carried forward; NI, no induction; PBO, placebo; PsAID, Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease; SLK, sonelokimab.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Laure Gossec has been paid as a speaker for AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB, has worked as a paid consultant for AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Janssen, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, has received grants/research support from AbbVie, Biogen, Lilly, Novartis, and UCB, Alexis Ogdie has worked as a consultant for AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Corrona, Gilead, GSK, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Spyre, Takeda, TREG, Pfizer, UCB, has received grants/research support from AbbVie (to Penn), Amgen (to Forward), BMS (to Forward), Janssen (to Penn), Novartis (to Penn), Pfizer (to Penn), Forward/National Databank for Rheumatic Diseases, NIH/NIAMS, Rheum Research Foundation, Alice B. Gottlieb has received honoraria as an advisory board member and consultant for Amgen, Lilly, Highlights Therapeutics, Janssen, Novartis, Sanofi, SunPharma, Takeda, Teva, UCB, and Xbiotech (stock options for RA), has received research/educational grants from, BMS, Janssen, MoonLake Immunotherapeutis, and UCB Pharma, (all paid to Mount Sinai School of Medicine), Fabian Proft has been paid as a speaker for AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Lilly, Hexal, Janssen, Medscape, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and UCB, has received consultancy payments from AbbVie, BMS, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB, has received grants/research support from Novartis, Lilly and UCB with payments made via my institution, Joseph F. Merola has been a consultant and/or investigator for Amgen, Astra-Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbvie, Dermavant, Lilly, Incyte, MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, Novartis, Janssen, UCB, Sanofi-Regeneron, Sun Pharma, Biogen, Pfizer and Leo Pharma, Nuala Brennan is a shareholder in MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, is an employee of MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, Alex Godwood is a shareholder of MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, is an employee of MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, Matthew R. Thomas has stock options in MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, is an employee of MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, Eva Cullen has presented at congresses as part of current employment with MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, is a shareholder of MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, is an employee of MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, Kristian Reich has been paid as a speaker for LEO Pharma, Lilly Pharma, Almirall S.A, AbbVie, and Janssen-Cilag, is a shareholder of MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, is an employee of MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, has worked as a paid consultant for LEO Pharma, Lilly, Almirall S.A, AbbVie, and Janssen-Cilag, has received grants/research support from LEO Pharma, Lilly, Almirall S.A, and AbbVie, Laura C. Coates has been paid as a speaker for AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB, has worked as a paid consultant for AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Enlivex, Janssen, MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda and UCB, has received grants/research support from Abbvie, Amgen, Janssen and UCB.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (