

Background: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation, vasculopathy, and fibrosis, with B cell activation playing a critical role in its pathogenesis [1]. Interleukin-40 (IL-40), primarily produced by activated B cells, has been implicated as a potential biomarker in autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, due to its role in inflammation and humoral immune responses [2]. The elevated expression of B cell-related molecules like IL-40 and BAFF in SSc suggests their involvement in fibrosis and disease progression.
Objectives: This study aims to evaluate the role of IL-40 in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis by assessing its relationship with clinical findings and disease activity and investigating the correlation between IL-40 levels and immunosuppressive therapies.
Methods: This study recruited 47 systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients meeting the 2013 ACR/EULAR classification criteria, categorized into three subgroups based on disease activity and immunosuppressive therapy status, alongside 30 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. Clinical assessments included symptoms, serological markers, and immunosuppressive therapy status, with IL-40 serum levels measured via ELISA from stored samples.
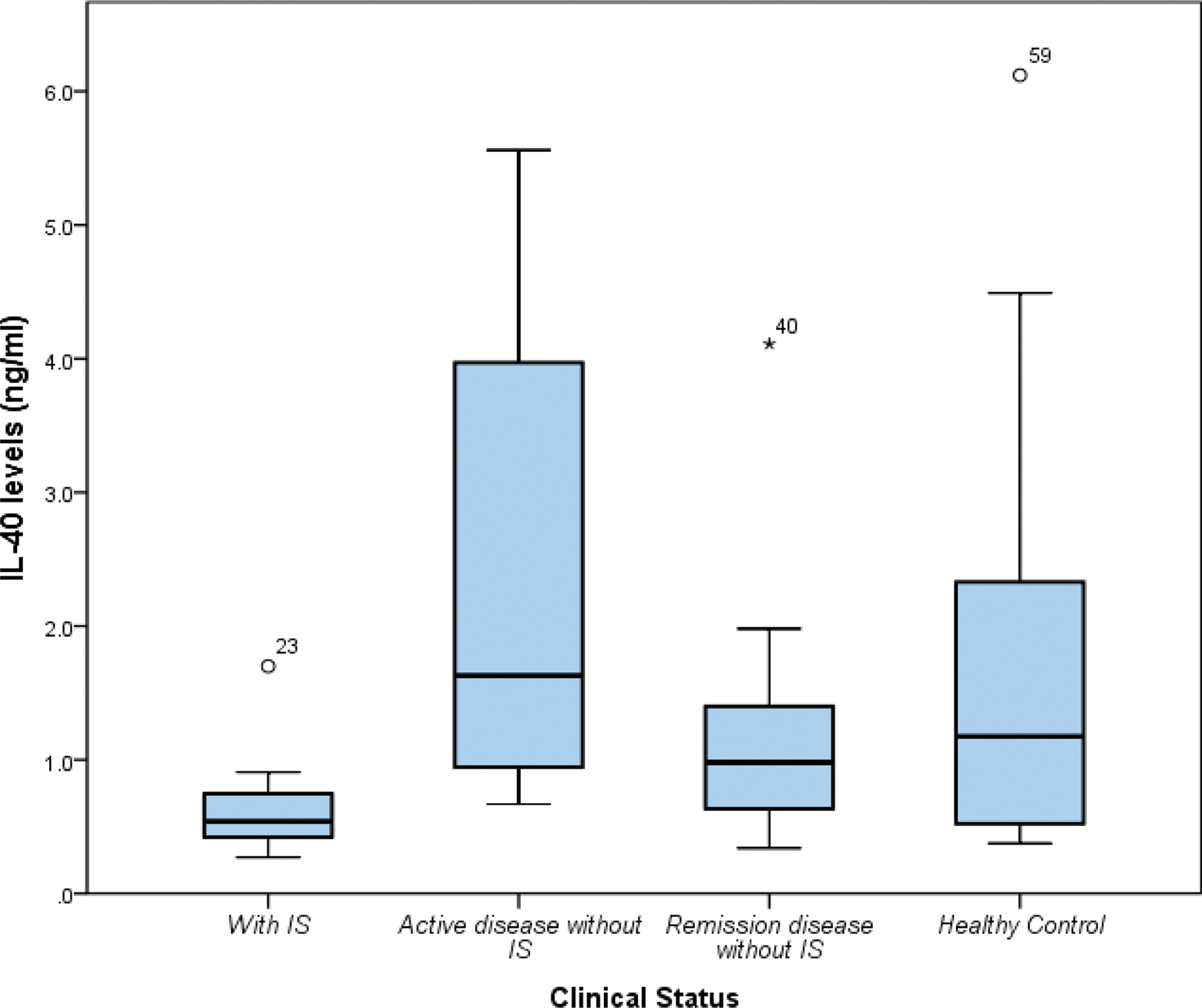
Results: This study evaluated 47 systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients, primarily female (93.6%), with a mean age of 44.7 years and median disease duration of 9 years. Patients were classified into diffuse SSc (44.7%), limited SSc (46.8%), and overlap syndrome (8.5%). Common manifestations included Raynaud phenomenon (93.6%), sclerodactyly (89.4%), interstitial lung disease (46.8%), and esophageal dysphagia (46.8%). Serologically, anti-nuclear antibody positivity was observed in 89.4%, anti-topoisomerase I in 61.7%, and anti-centromere antibody in 19.1%. Patients were categorized into three subgroups based on disease activity and immunosuppressive therapy status. The patients currently receiving immunosuppressive therapies included those on mycophenolate mofetil (n=13), glucocorticoids (n=9), azathioprine (n=2), cyclophosphamide (n=1), and rituximab (n=1). These are given in Table 1. IL-40 levels differed significantly across clinical groups. Patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy (IS) had lower IL-40 levels than those without IS (0.54 vs. 1.15 ng/ml, p=0.001). IL-40 levels were higher in active disease without IS (1.63 ng/ml) compared to remission without IS (0.98 ng/ml, p=0.031). IL-40 levels in healthy controls were comparable to those in remission without IS. These are given in Figure 1. These findings suggest IL-40 as a potential biomarker for SSc activity, reflecting the interplay of disease activity and immunosuppressive therapy effects.
Conclusion: Our study found that IL-40 levels were significantly lower in SSc patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy compared to those not receiving such treatment and healthy controls. Additionally, IL-40 levels were elevated in patients with active disease who were not on immunosuppressive therapy. These findings suggest that IL-40 may serve as a biomarker for assessing disease activity in SSc and could also provide insights into the effectiveness of immunosuppressive therapies targeting B cells.
REFERENCES: [1] Denton CP, Khanna D. Systemic sclerosis. The Lancet . 2017;390:1685–99. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30933-9.
[2] Catalan-Dibene J, Vazquez MI, Luu VP, et al. Identification of IL-40, a Novel B Cell-Associated Cytokine. J Immunol . 2017;199:3326–35. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700534.
Patients’ current clinical and treatment status.
| Clinical and Treatment Status (Current) | SSc patients (n=47) |
|---|---|
| Active disease without immunosuppressive therapy (n:11 ) | 11 (23.4) |
| Digital ulcer, n(%) | 7 (63.6) |
| Interstitial lung disease, n(%) | 3 (27.3) |
| Inflammatory arthritis, n(%) | 1 (9.1) |
| Remission disease without immunosuppressive therapy (n:21 ) | 21 (44.7) |
| Active or remission disease with immunosuppressive therapy (n:15 ) | 15 (31.9) |
| Glucocorticoid, n(%) | 9 |
| Azathioprine, n(%) | 2 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil, n(%) | 13 |
| Cyclophosphamide, n(%) | 1 |
| Rituximab, n(%) | 1 |
Comparison of IL-40 Levels Among different SSc patients and healthy group.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (