

Background: The first biosimilar rituximab (RTX-B), Truxima® was launched in our department in October 2017. Patients therefore underwent non-medical switch (i.e. changed for reasons other than the patient’s health and safety). We previously showed that non-medical switch from originator rituximab (RTX-O) to RTX-B was largely effective in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with comparable 18-month retention rates between those who switched vs remained on RTX-O, 76% and 82% respectively [1]. However, the uptake of non-medical switch in autoimmune connective tissue diseases and vasculitis (CTD-VAS) has been slow due to a concern with cross-reactivity of antibodies. Data pertaining to effectiveness of switching between biosimilars are also lacking.
Objectives: To evaluate the effectiveness of non-medical switch from RTX-O to RTX-B or between biosimilars RTX in CTD-VAS.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective observational cohort study of RMD patients in a single centre between October 2017 (Index date) and November 2024. During this period, all patients were encouraged to switch to RTX-B (Truxima®) unless declined by the patient or specified by the treating clinician. Furthermore, between 2021-2023, patients on Truxima® were switched to Rixathon® and then reverted to Truxima® in 2024 due to contractual agreement. Due to differences in disease activity tools, clinical responses were graded into full response; partial; and non-response. Other measures of effectiveness include the depth of CD20+ cells depletion by highly sensitive flow cytometry and 5-year RTX retention rate between patients who underwent non-medical switch (Group 1) vs those who remained on RTX-O or started on RTX-B (Group 2).
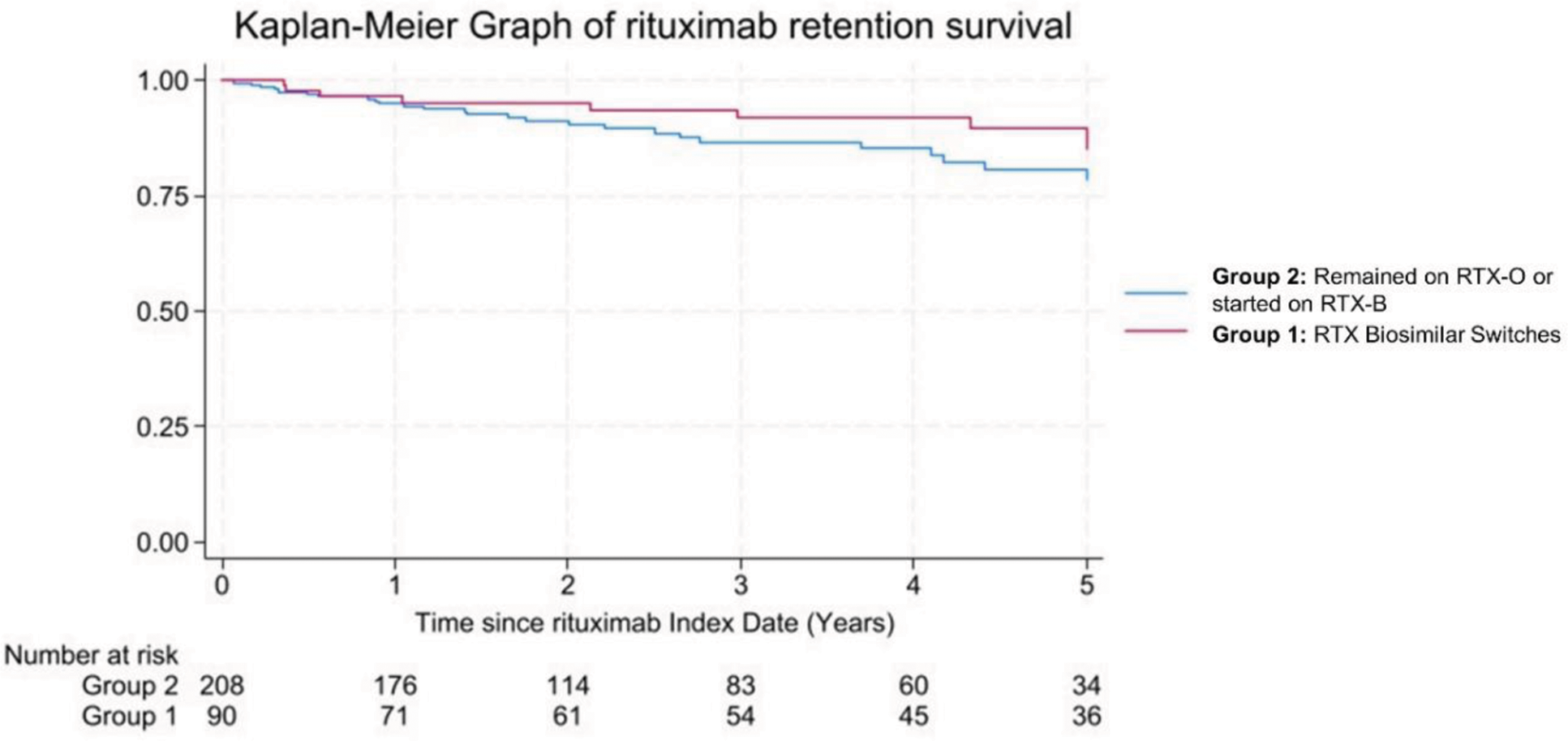
Results: At Index date, of 827 RMD patients treated with RTX, 300 (36%) were given for CTD-VAS, while the remaining for RA. Of these, 90/300 (30%) underwent non-medical switch, Group 1 [RTX-O to RTX-B = 61 (68%); between biosimilars = 29 (32%)]. They had mean (SD) age 51 (15) years, 61 (72%) were female, 64 (71%) had European ancestry, median (IQR) SLE duration of 8.7 (5-15) years, median (range) number of comorbidities of 1 (0-5), and diagnoses were SLE (53%), AAV (31%), Sjogren (4%), Myopathies (3%), Scleroderma (1%) and other CTD (8%). 16/300 (5%) patients remained on RTX-O, while 194/300 (65%) initiated treatment with RTX-B; therefore Group 2 = 210/300 (70%). At the last follow-up, of 90 patients in Group 1, 78/90 (87%) remained on RTX-B including 9/78 who underwent further biosimilar switches due to contractual agreement without problems and 1/78 (3%) reverted to the previous RTX-B brand due to development of a rash following biosimilar switch. 5/90 (6%) of patients on RTX-B reverted to RTX-O and regained response. Reasons were infusion reaction=1, serum sickness=1; neutropenic sepsis 5 days post-RTX switch=1; skin lesion=1; incomplete depletion and inferior response=1. Of 87/90 and 77/90 patients in Group 1 with paired clinical response and B-cells data in the RTX cycle before and after switch respectively, there was no difference in response rate (partial or full) and CD20+ cell complete depletion, p=0.289 and p=1.00 respectively (McNemara’s test). The delta difference in CD20+ cells depletion at 2 weeks from RTX infusion between before and after switch were no different, p=0.995 (Wilcoxon Sign Ranked Test). At Index Date, patients in Group 2 had shorter disease duration, less number of RTX cycles, and higher daily oral prednisolone dose than those in Group 1. At 5 years, 9/90 (10%) patients discontinued RTX in Group 1 [inefficacy=7 including 2 who reverted to RTX-O); 2 deaths due to pneumonia=1 and COVID pneumonitis=1], while in Group 2, 28/210 (13%) discontinued therapy [inefficacy=16; side effects=3; and deaths due to cardiac=4, pneumonia=2; pulmonary fibrosis=2; and multi-organ failure=1]. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed no difference in 5-year RTX retention survival between Group 1 and Group 2; HR 0.71 (95% CI 0.30-1.71), p=0.448, adjusted for disease duration, number of RTX cycles and oral prednisolone dose (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Our findings support the non-medical switch either from RTX-O to RTX-B or between biosimilars in CTD-VAS with no difference in clinical response and the depth of B-cell depletion before and after switch. 5-year rituximab retention rate was very good regardless of non-medical switch and appeared higher than in RA. Given its low cost and durability, future studies should assess the cost-effectiveness of first-line use of rituximab biosimilars in patients with CTD-VAS.
REFERENCES: [1] Melville A et al. Rheumatology. 2021 Aug 2;60(8):3679-3688.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Rusyai Zalynda Ramli: None declared, Charles Joseph Bithell: None declared, Mohmedshahid Patel: None declared, Paul Emery Roche, Shouvik Dass: None declared, Edward M. Vital Roche, Roche, Sandoz, Md Yuzaiful Md Yusof Roche.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (